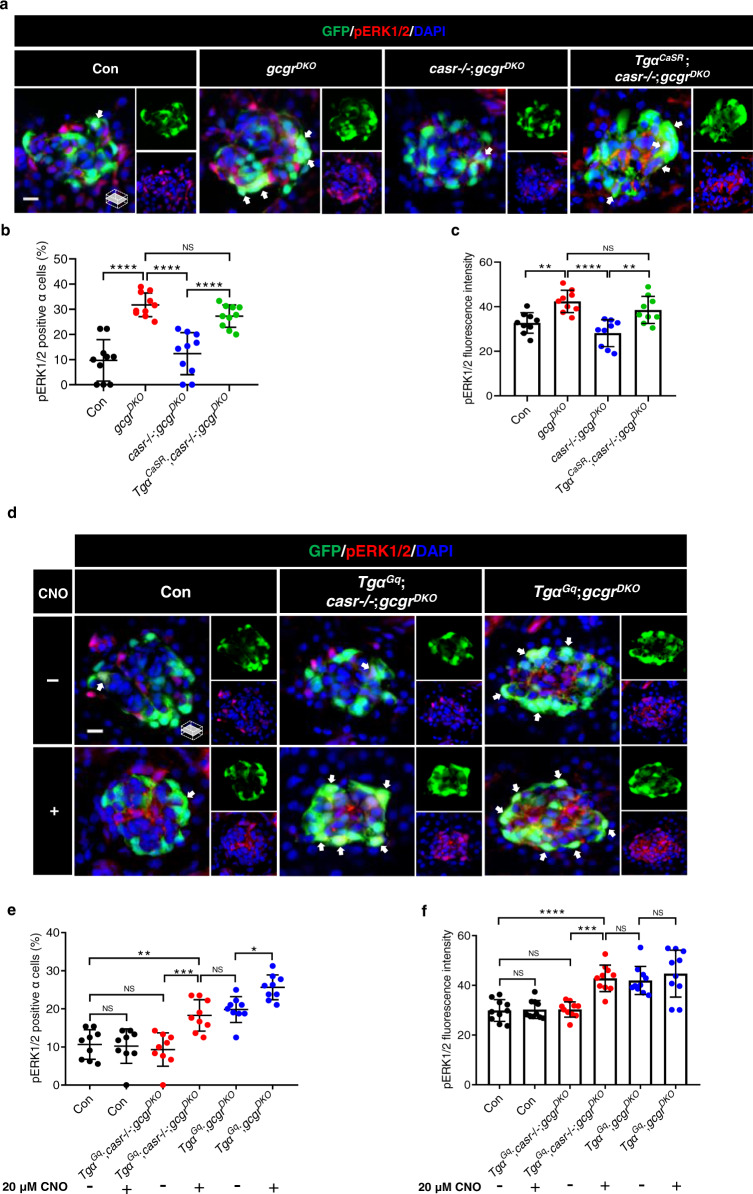
Fig. 7
a Representative images of pERK1/2 and GFP immunofluorescence in islet sections of control, gcgrDKO, casr−/−;gcgrDKO and TgαCaSR;casr−/−;gcgrDKO larvae at 5 dpf. The pERK1/2 signal in α cells is indicated by arrows, primary antibody: Anti-pERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) (1:150, rabbit); secondary antibody: Alexa Fluor 568 (1:1,000, goat anti-rabbit) (scale bar, scale bar, 8 μm). b Quantification of the percentage of pERK1/2 positive α cells in control, gcgrDKO, casr−/−;gcgrDKO and TgαCaSR;casr−/−;gcgrDKO larvae at 5 dpf (data represent the means ± SD, n = 10 for each group). c Quantification of pERK1/2 fluorescence intensity in α cell of control, gcgrDKO, casr−/−;gcgrDKO, and TgαCaSR;casr−/−;gcgrDKO larvae at 5 dpf (Data represent means ± SD, n = 9 for each group). d Representative images of pERK1/2 and GFP immunofluorescence in islet sections of control, TgαGq;casr−/−;gcgrDKO and TgαGq;gcgrDKO larvae at 5 dpf. The larvae were treated with 20 μM CNO or vehicle for 48 h. The pERK1/2 signal in α cells is indicated by arrows, primary antibody: Anti-pERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) (1:150, rabbit); secondary antibody: Alexa Fluor 568 (1:1000, goat anti-rabbit) (scale bar, 8 μm). e Quantification of the percentage of pERK1/2 positive α cells in control, TgαGq;casr−/−;gcgrDKO and TgαGq;gcgrDKO larvae treated with 20 μM CNO or vehicle for 48 h at 5 dpf (data represent the means ± SD, n = 9 for each group). f Quantification of the pERK1/2 fluorescence intensity in α cells of control, TgαGq;casr−/−;gcgrDKO and TgαGq;gcgrDKO larvae treated with 20 μM CNO or vehicle for 48 h at 5 dpf (data represent the means ± SD, n = 10 for each group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS indicates no significant difference (one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, the quantifications represent individual islet sections). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.