Fig. 1
STX4 germline variants in patients
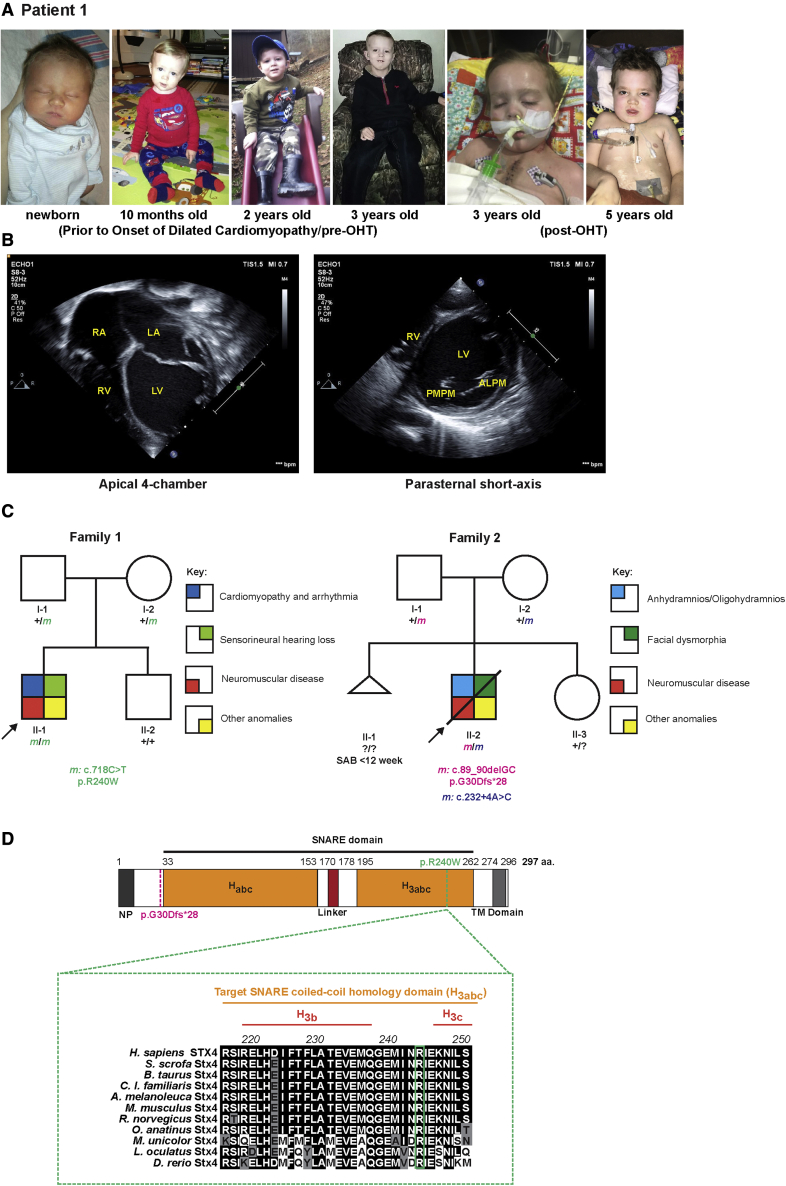
(A) Left to right: Photographs of patient 1 taken before and after onset of DCM, and pre- and post-OHT.
(B) Echocardiograms at onset of patient?s admission due to heart failure. Left: Apical 4-chamber view at end-diastole showed severely dilated, thin-walled left ventricle and severely dilated left and right atria. Right: parasternal short-axis view at the level of the mitral valve at end-diastole showed severely dilated, thin-walled left ventricle. The patient had severe biventricular systolic dysfunction, and evidence for diastolic dysfunction (biatrial dilation). ALPM, anterolateral papillary muscle; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; PMPM, posteromedial papillary muscle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.
(C) Pedigree segregating the homozygous STX4 c.718C > T; p.R240W variant in family 1 and the c.89_90delGC; p.G30Dfs?28 and c.232+4A > C alleles in family 2. m, variant allele; ?, unknown carrier; SAB, spontaneous abortion without further data.
(D) Alignment of portion of the STX4 sequences containing the human variant. There is a high degree of conservation overall for STX4 homologues. For instance, mouse Stx4 and zebrafish stx4 respectively share 95.3% and 75.3% amino acid conservation with human STX4. Dashed-magenta line indicates position of p.G30Dfs?28 allele. Dashed-green line indicates the position of the p.R240W variant and expanded residue sequence indicates the conservation of this residue among the selected vertebrates. The residue positions indicate domain boundaries of the 297 amino acid human STX4 protein.61 Black highlights indicate amino acids that are conserved, gray highlights residues that are chemically similar (conservative), and white highlights display non-conservative variants. Habc, antiparallel three-helix bundle stabilization domain, H3abc, coiled-coil SNARE homology domain; NP, N-terminal peptide, TM, transmembrane.