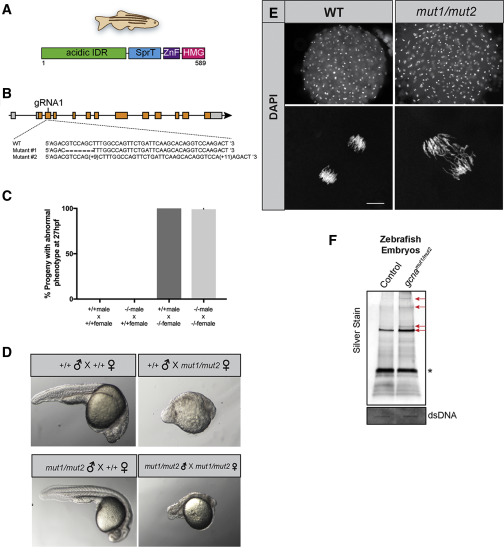
Fig. 6 GCNA Function Is Conserved in Vertebrates (A) Domain structure of the zebrafish GCNA protein. (B) Organization of the zebrafish gcna gene showing the lesions in the mut1 and mut2 alleles. (C and D) Zebrafish embryos derived from mutant gcna mutant females exhibit profound maternal-effect defects, regardless of the paternal genotype. (C) Quantification of defects and (D) representative embryos from indicated crosses. (E) Fixed, DAPI-stained embryos derived from mutant gcna mutant females exhibit asynchronous divisions and extensive chromosome bridges during early development. For +/+M;+/+F: n = 142; -/-M; +/+F: n = 114; +/+M; -/-F: n = 173; -/-M; -/-F: n = 75. Scale bar represents 10 ?m. (F) RADAR was performed on zebrafish embryos, as described in Figures 4A and 4B. Samples were normalized to dsDNA input, separated by SDS-PAGE, and silver stained. Red arrows mark bands increased in gcna mutants. ? marks benzonase.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 52(1), Bhargava, V., Goldstein, C.D., Russell, L., Xu, L., Ahmed, M., Li, W., Casey, A., Servage, K., Kollipara, R., Picciarelli, Z., Kittler, R., Yatsenko, A., Carmell, M., Orth, K., Amatruda, J.F., Yanowitz, J.L., Buszczak, M., GCNA Preserves Genome Integrity and Fertility Across Species, 38-52.e10, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell