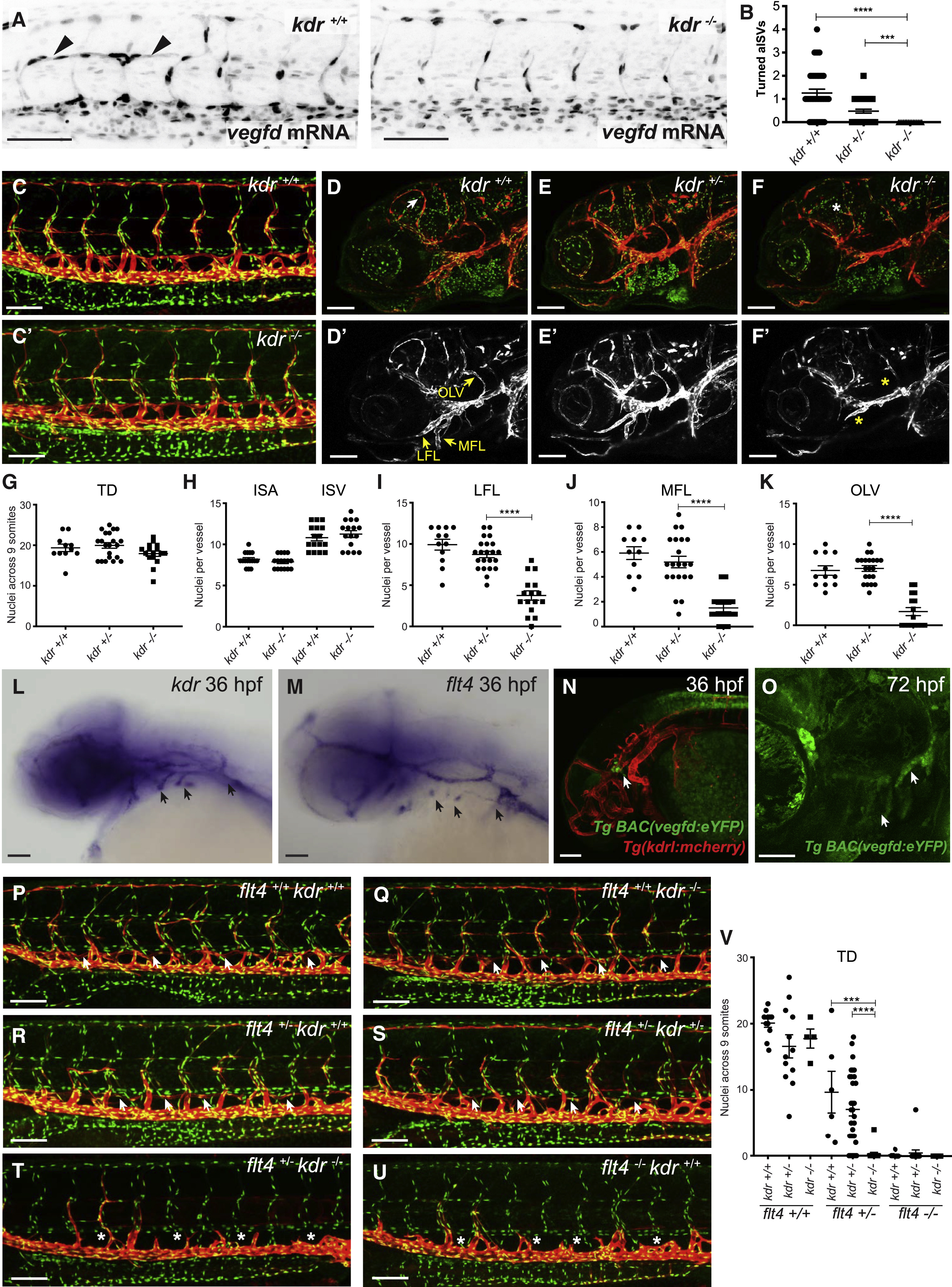
Fig. 4
Kdr Interacts with zVegfd In Vivo and Regulates Craniofacial Lymphangiogenesis but Not Development of the Thoracic Duct
(A) Confocal images of 30-hpf Tg(fli1a:nEGFP) embryos injected with vegfdmRNA showing turned aISVs (arrowheads) in wild-type but not in kdrhomozygous mutant siblings.
(B) Quantification of turned aISVs in wild-type (n = 39), kdruq38bh heterozygous (n = 42), and homozygous mutant (n = 15) embryos at 30 hpf.
(C and C′) Analysis of thoracic duct (TD) development. Confocal images of 5-dpf Tg(fli1a:nEGFP);Tg(−5.2lyve1b:dsRed) transgenic embryos produced by in-crossing kdruq38bh carriers. TD development in kdruq38bh mutant embryos (C′) is equivalent to wild-type (C) siblings. Red denotes Lyve1-positive lymphatics and green denotes Fli1-positive nuclei.
(D–F) Analysis of facial lymphatic development. Images showing the facial region of 5-dpf Tg(fli1a:nEGFP);Tg(−5.2lyve1b:dsRed) transgenic embryos. Genotypes in (D) and (D′) are kdr+/+, (E) and (E′) kdr+/−, and (F) and (F′) kdr−/−. Red denotes Lyve1-positive lymphatics and green denotes Fli1-positive nuclei. White arrow indicates mural LEC loop and white asterisk denotes its absence.
(D′–F′) lyve1b:dsRed only; white anatomical structures are Lyve1-positive lymphatics. Yellow arrows indicate normal lateral facial lymphatics (LFLs), medial facial lymphatics (MFLs), and otolithic facial lymphatics (OLVs). Yellow asterisks indicate where there are reductions in LEC numbers in these vessels.
(G) There was no significant difference in the number of nuclei in the TD when homozygous kdruq38bh mutants were compared to heterozygous and wild-type siblings (kdr+/+ embryos n = 11; kdr+/− n = 21; kdr−/− n = 16).
(H) There was no significant difference in the number of nuclei in ISAs or ISVs when homozygous kdruq38bh mutants were compared to wild-type siblings (n = 16, 2 ISAs or ISVs from 8 embryos).
(I–K) Significant differences in LFL (I), MFL (J), and OLV (K) LEC numbers were observed when homozygous kdruq38bh mutant embryos (n = 16) were compared to kdruq38bh heterozygous (n = 22) or wild-type (n = 12) embryos. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
(L and M) In situ hybridization using probes complementary to kdr (L) and flt4(M) in 36-hpf embryos reveals robust expression in the region where lymphatic sprouts emerged from the common cardinal vein and the primary head sinus (arrows).
(N and O) Confocal images of the TgBAC(vegfd:eYFP)uq42bh; Tg(kdrl:mcherry)transgenic line at 36 hpf (N) and TgBAC(vegfd:eYFP)uq42bh at 72 hpf (O) reveal expression of vegfd in the craniofacial region close to where lymphatic sprouts emerge from the primary head sinus (arrows).
(P–U) Confocal images of 5-dpf Tg(fli1a:nEGFP);Tg(−5.2lyve1b:dsRed) transgenic embryos produced by in-crossing kdruq38bh/flt4hu4602 carriers. Genotypes in (P) are flt4+/+ kdr+/+, (Q) flt4+/+ kdr−/−, (R) flt4+/− kdr+/+, (S) flt4+/− kdr+/−, (T) flt4+/− kdr−/−, and (U) flt4−/− kdr+/+. In flt4hu4602 heterozygous embryos, loss of kdruq38bhresulted in a complete failure of the TD to form (T) and were phenotypically indistinguishable from flt4hu4602 mutant embryos. Arrows indicate TD and asterisks its absence.
(V) Quantification of TD nuclei for embryos referred to in (P)–(U) (flt4+/+/kdr+/+embryos n = 11; flt4+/+/kdr+/− n = 12; flt4+/+/kdr−/− n = 4; flt4+/−/kdr+/+ n = 6; flt4+/−/kdr+/− n = 31; flt4+/−/kdr−/− n = 16; flt4−/−/kdr+/+ n = 8; flt4−/−/kdr+/− n = 14; flt4−/−/kdr−/− n = 8).
All scale bars in this figure represent 100 μm except for (O), in which the bar denotes 50 μm. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM.