Fig. 3
Fig. 3
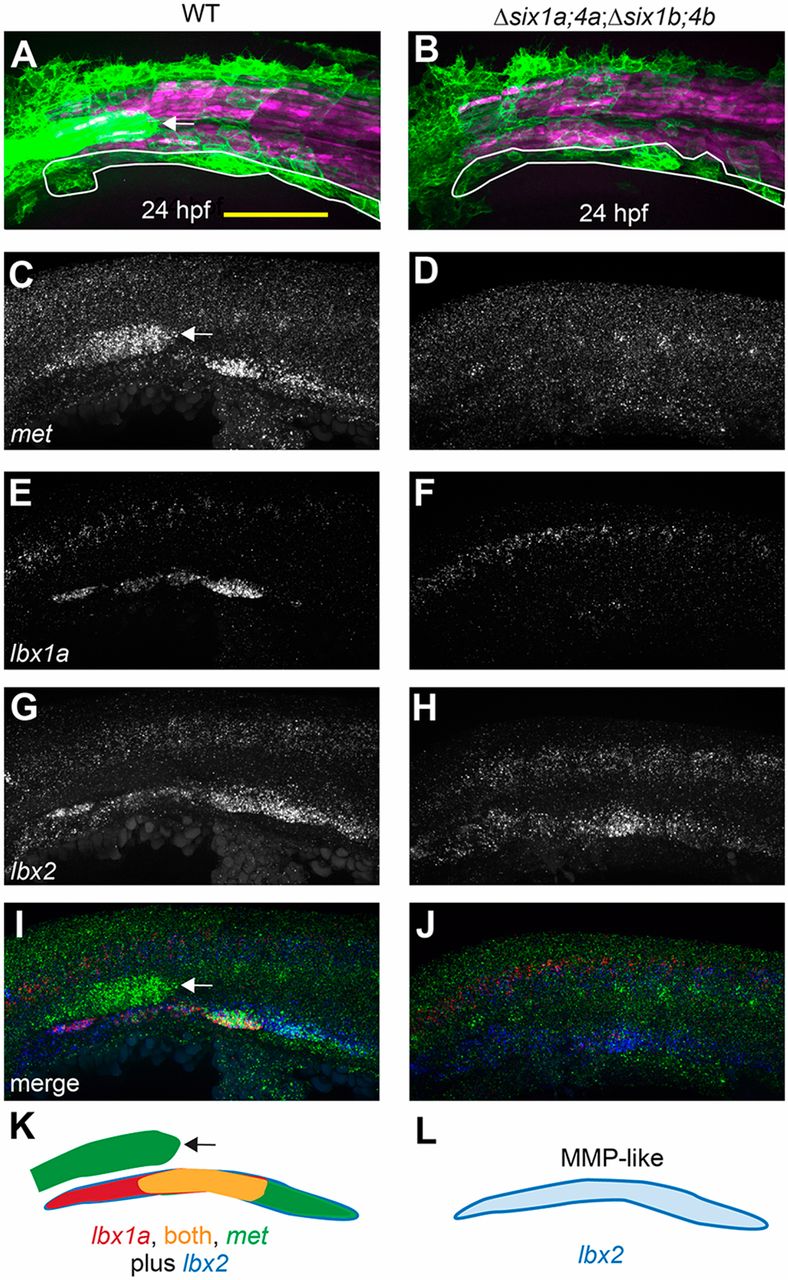
six1/six4 gene function is required to fully specify MMPs. (A,B) Muscle fibers and MMPs, visualized at 24?hpf using six1b:lyn-GFP (green) and mylpfa:mCherry (magenta) transgenes. Prior to MMP migration onset, Δsix1a;4a;Δsix1b;4b mutant trunk muscle appears normal (also see Fig. S3) and MMP-like cells are positioned at the ventral edge of the somite (white outline). (C-J) Fluorescent in situ hybridization showing met (C,D), lbx1a (E,F), lbx2 (G,H), or overlay of met (green), lbx1a (red), and lbx2 (blue) (I,J), at 24?hpf. (K,L) Schematics of gene expression patterns in wild-type (K) and Δsix1a;4a;Δsix1b;4b mutant (L) MMPs at 24?hpf. In 24?hpf wild-type embryos, lbx2 (blue) is broadly expressed whereas lbx1a (red) is prominent in anterior MMPs and met (green) is prominent in posterior MMPs; however, by 36?hpf, met is expressed in all three streams (Fig. S4N, S6E). In contrast, lbx1a and met are not expressed in 24?hpf Δsix1a;4a;Δsix1b;4b mutants, but lbx2-positive MMP-like cells are present. six1b:lyn-GFP and met expression are also seen in the lateral line primordium (arrow in A,C,I,K) of wild type but not quadruple mutants, consistent with the loss of this structure in Δsix1b;4b and Δsix1a;4a;Δsix1b;4b mutants (see also Fig. 2A,F and Fig. S3G,H).Yellow shading represents expression of both lbx1a and met. Scale bar: 100?µm.