Fig. 3
Fig. 3
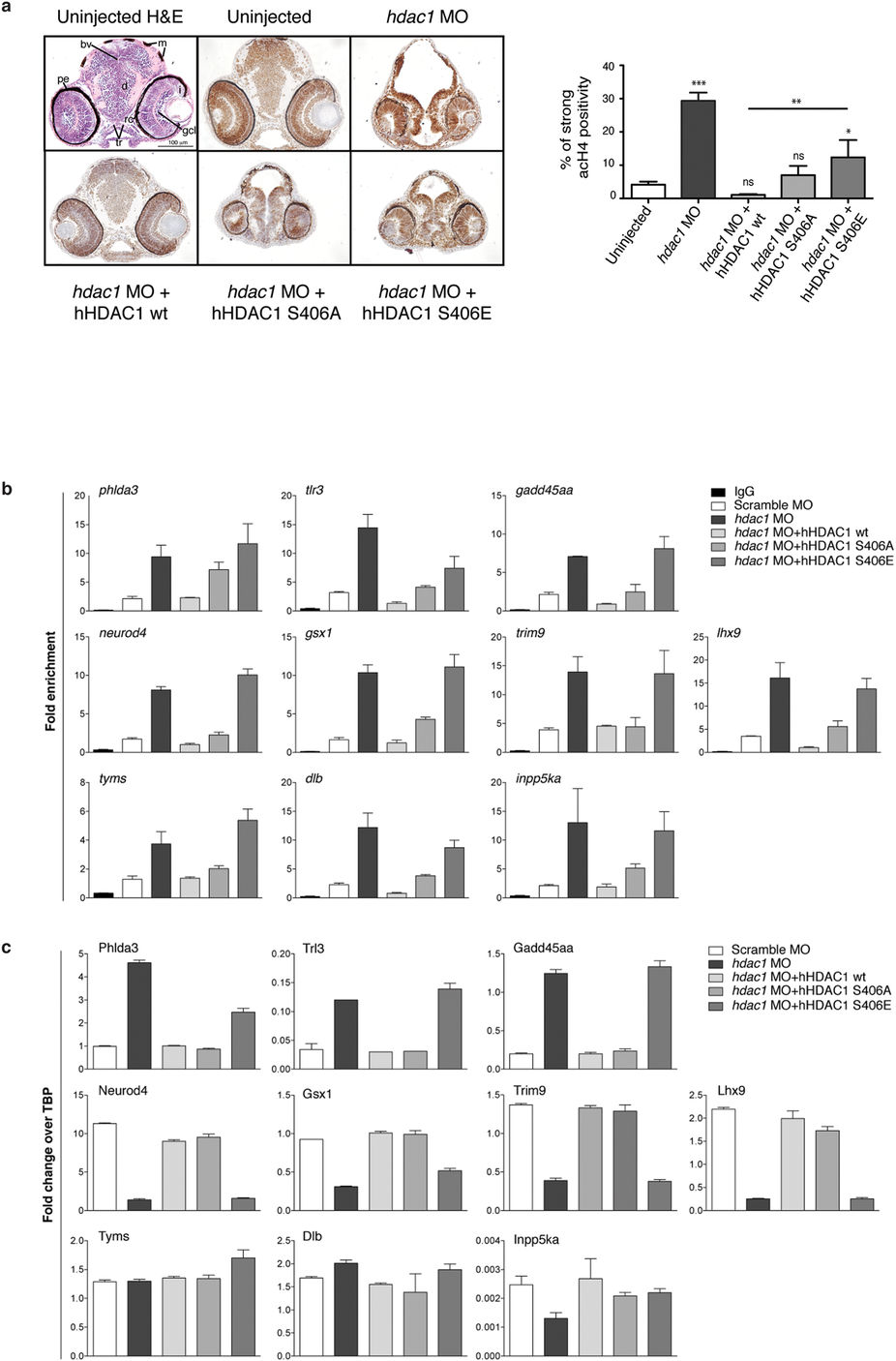
Aurora dependent phosphorylation of HDAC1 modulates histone acetylation and the expression of a core of CNS-related genes in zebrafish embryos.
(a?c) Embryos were injected, at one cell stage, with Scramble MO (b,c) or hdac1 MO alone or in combination with hHDAC1 aurora phospho mutants and collected at 72 hpf. (a) Immunohistochemistry staining with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E uninjected panel: d: diencephalon; pe: pigmented epithelium; tr: trabecular; rc: rods and cones; gcl: ganglion cell layer; i: iris; m: melanocytes; bv: brain ventricle) and with haematoxylin (blue) and anti-acetylated histone antibody (brown). Quantification was performed and expressed as percentage of strong positive histone H4 acetylated pixels?±?SEM in the diencephalon area. All samples were compared to uninjected sample and in particular hdac1 MO?+?hHDAC1 S406E was also compared to hdac1 MO?+?hHDAC1 wt. **P value?<?0.01; ***P value?<?0.001; ns: not significant. Scale bar corresponds to 100??m. (b) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis of H3K27 acetylated cis-regulatory regions of Hdac1-regulated genes. Representative data from at least two independent experiments are shown; RTqPCR data are presented as mean?±?S.E.M. of three replicates. (c) Gene expression analysis of Hdac1-regulated genes. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown; RTqPCR data are presented as mean?±?S.E.M. of three replicates. TBP is used as housekeeping.