Fig. S3
Fig. S3
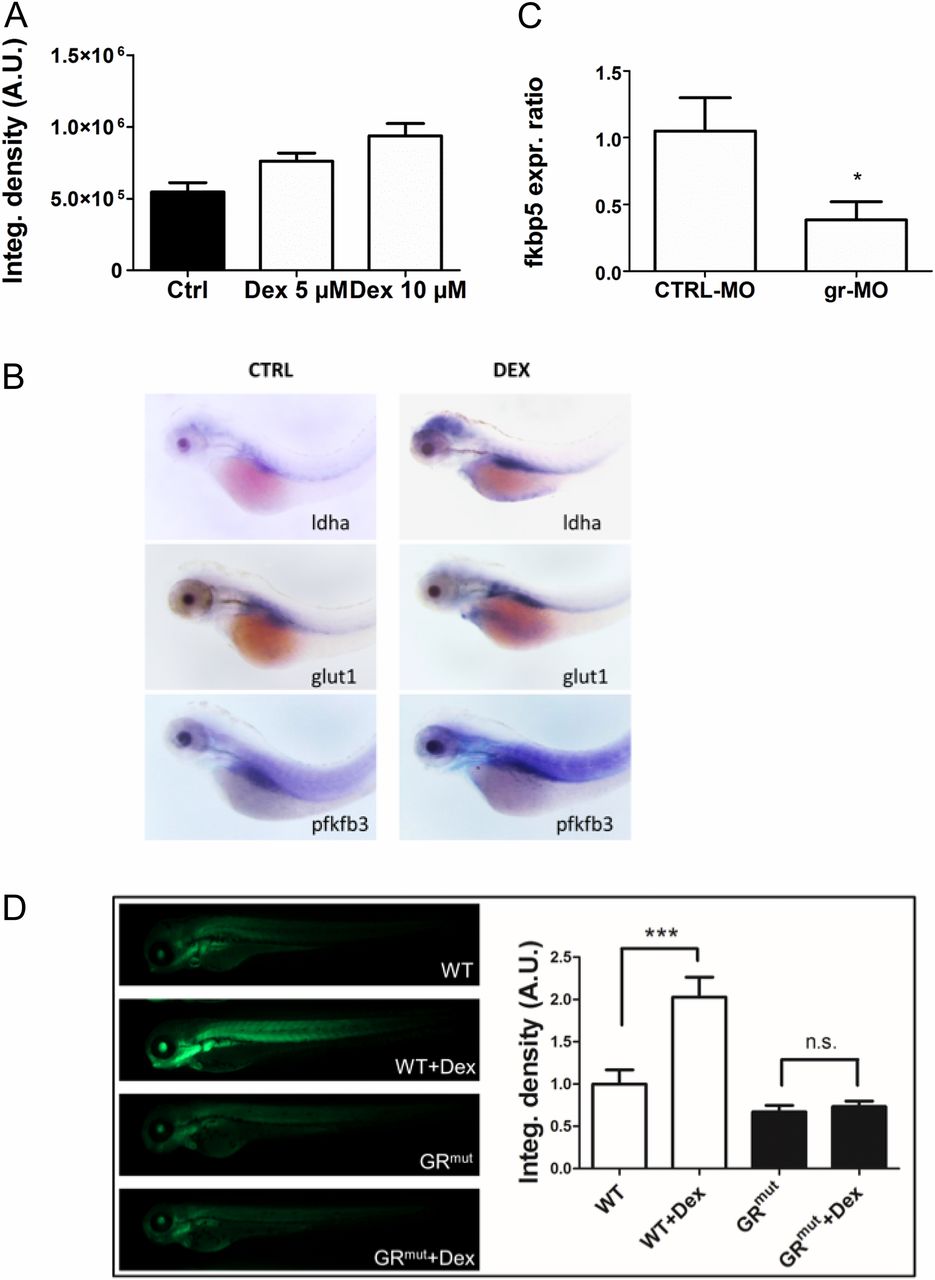
DEX induces Hif-1 pathway activation and expression of glycolytic regulators and is GR-dependent. (A) Histograms showing the average values of the integrated density of fluorescence in 72-hpf Tg(4xhre-tata:eGFP)ia21 embryos treated with different doses of DEX. DEX incubation induces a dose-dependent activation of the Hif-1 pathway as shown by the increase of the 4xhre-tata transgene expression. A.U., arbitrary units. (B) In situ hybridization for glycolytic regulators ldha, glut1, and pfkfb3 showing increased expression after DEX treatment. (Magnification: 17.5×.) (C) Fold changes in gene expression of fkbp5 in 72-hpf embryos injected with gr-MO and CTRL-MO compared with nontreated/noninjected control (set at 1). Real-time PCR analysis revealed that the expression of fkbp5 was significantly reduced in gr-MO?injected embryos, confirming the ability of gr-MO to impair the expression of the glucocorticoid receptor. (D, Left) Images of 72-hpf Tg(4xhre-tata:eGFP)ia21 in wild-type and GR CRISPR mutant background treated with 10 ?M DEX in DMSO for 24 h or with vehicle control. (Magnification: 10×.) (Right) Quantification of GFP reporter fluorescence, showing that the HRE reporter failed to respond in the GR mutant background. Generation of this GR mutant is described in SI Text.