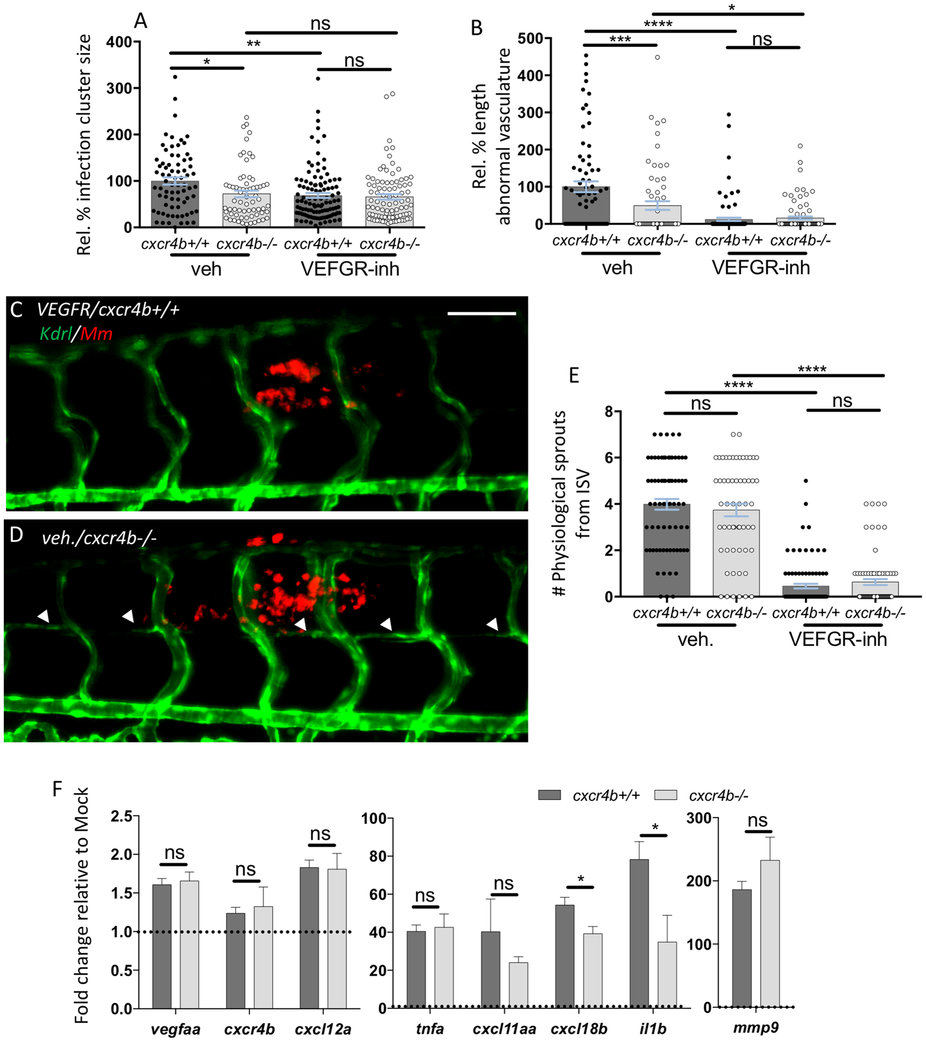
Fig. 4
Fig. 4
Deficient granuloma vascularisation in cxcr4b mutation does not strictly depend on aberrant Vegf signalling or attenuated expression of inflammatory genes.
(A,B) cxcr4b deficiency reduced granuloma expansion to a similar extent as blockade of Vegf signalling (VEGFR-inh, treatment with Sunitinib) (A), although Vegf inhibition can more severely affect angiogenesis. (B). Data are analysed as in Fig. 2A,B. Experiments were performed in 2 replicates (cumulated in the graphs). Total number of granulomas analysed: 73 (vehicle-cxcr4b+/+), 66 (vehicle-cxcr4b?/?), 109 (VEGFR-inhibitor-cxcr4b+/+), 88 (VEGFR-inhibitor-cxcr4b?/?). C?E Inhibition of Vegf signalling (C), but not depletion of cxcr4b (D), severely affects physiological angiogenesis. Quantification in E was performed by counting the number of sprouts from intersegmental vessels (ISV) from images encompassing 6?7 somites in the trunk region (as represented in C,D). Experiment was performed in 2 replicates (cumulated in the graph). Total number of region of interest analysed: 73 (vehicle-cxcr4b+/+), 59 (vehicle-cxcr4b?/?), 93 (VEGFR-inhibitor-cxcr4b+/+), 77 (VEGFR-inhibitor-cxcr4b?/?). Scale bar: 100??m. (F) At 5 dpi, Cxcr4b does not exert a transcriptional control on vegfaa expression, but affects the inflammatory response to mycobacterial infection, in particular by dampening il1b expression. qRT-PCR were performed whole mount from pools of at least 10 embryos (4 replicates). Data represent fold changes of Mm infection groups relative to their mock injection (2% PVP in PBS) control group (set to 1, dotted line). No significant differences in basal expression levels were found between mutants and wt for the analysed genes.