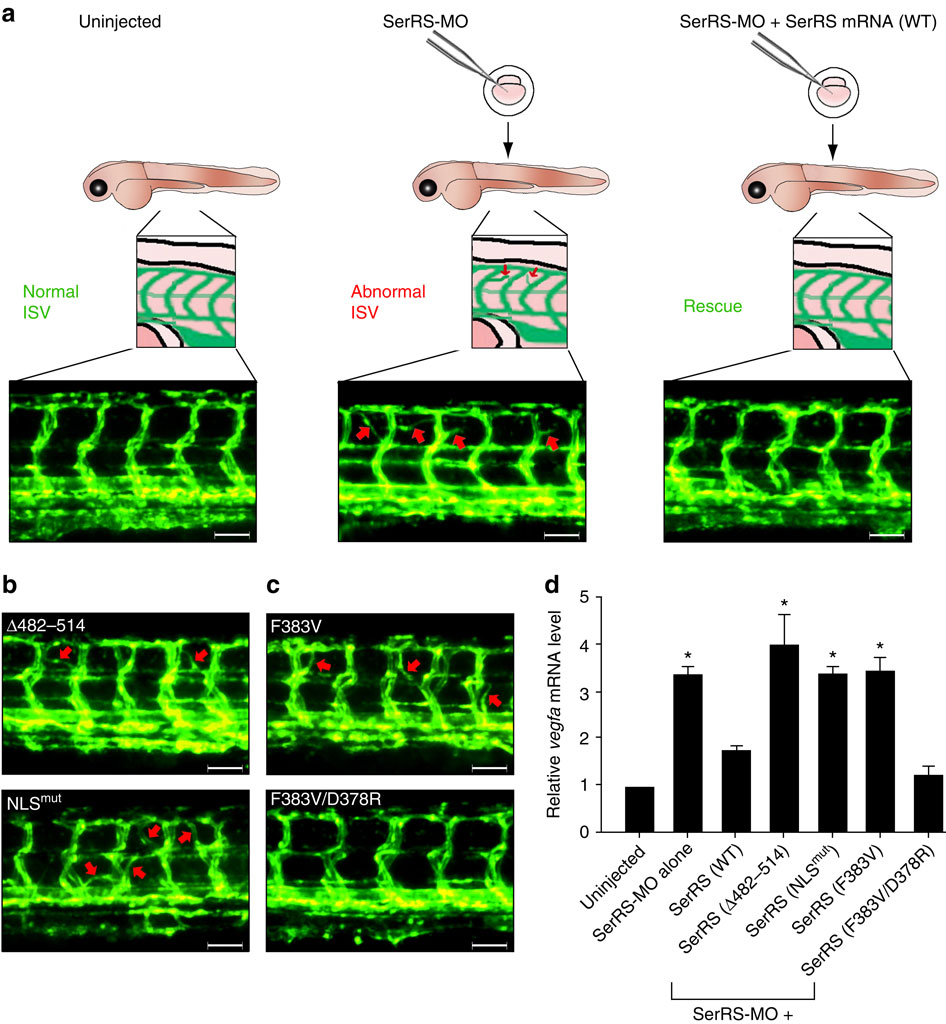
Fig. 6
Rescue experiments in zebrafish demonstrating the role of UNE-S in vascular development. (a) Illustration of the phenotype rescue experiment in zebrafish. The SerRS morpholino (SerRS-MO, ~5 ng per embryo) was injected into the yolk of zebrafish embryos (1- to 2-cell stage) to produce a model of intersegmental vessel (ISV) abnormality. Co-injection of SerRS-MO with the WT human SerRS mRNA (~250 pg per embryo) rescued the aberrant ISV branching. The ISV development is recorded at 72 h post fertilization and the abnormal ISV branches are indicated by red arrows. (b) Co-injection of SerRS-MO with the NLS-deleted Δ482-514 or NLSmut human SerRS mRNA did not rescue the aberrant ISV branching. (c) Co-injection of SerRS-MO with F383V human SerRS mRNA did not, whereas with F383V/D378R SerRS mRNA did, rescue the aberrant ISV branching. (d) The effect of SerRS nuclear localization on VEGFA transcription. Semiquantitative RT?PCR analysis to evaluate vefga mRNA levels in 72-hpf zebrafish embryos injected with SerRS-MO alone or SerRS-MO together with WT or mutant human SerRS mRNAs. Relative vegfa mRNA levels represented as fold increase (meanħs.e.m., n=3, *P<0.05 (Student′s t-test)) over uninjected control samples, after normalization to the levels of β-actin mRNA. Scale bars in this figure correspond to 100 µm.