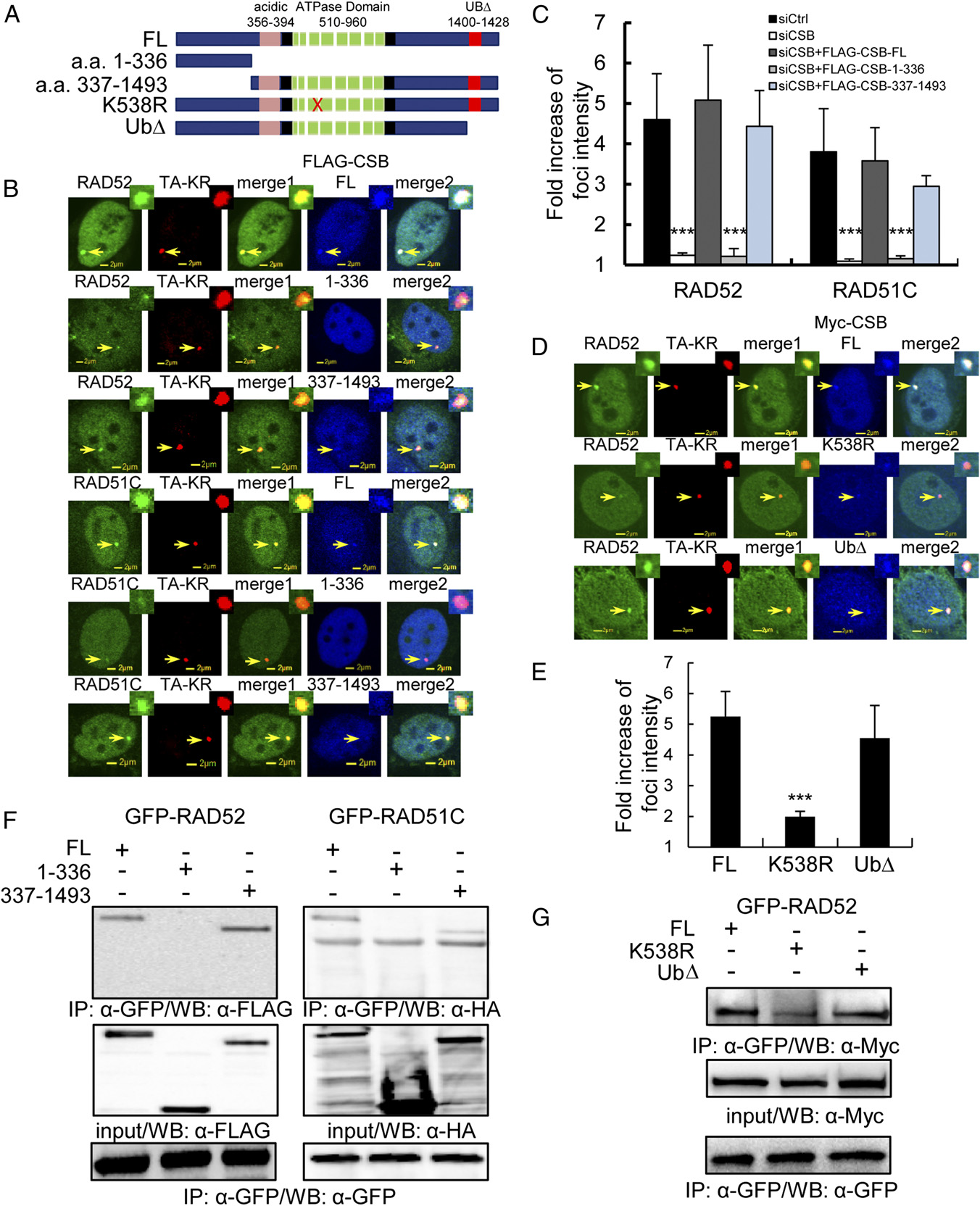
Fig. 5
The recruitment of CSB at TA-KR damage sites is via its C terminus and depends upon its ATPase activity. (A) Scheme of CSB mutants and deletions used in the study. (B) CSB aa 337?1493 is recruited to sites of TA-KR after damage. GFP-RAD52 or RAD51C, CSB or the indicated CSB mutant, and TA-KR were transfected into siCSB pretreated U2OS-TRE cells. The recruitment of GFP-RAD52 or RAD51C (green) and CSB (blue) at TA-KR is shown 30 min after KR activation. (C) CSB aa 337?1493 complements the recruitment of RAD51C and RAD52 after damage. The fold increase of foci intensity of GFP-RAD52 or RAD51C at TA-KR damage sites is quantified (n = 10). (D) The recruitment of GFP-RAD52 or RAD51C (green) and CSB K538R or Ub? (blue) at TA-KR is shown 30 min after KR activation. (E) CSB UbΔ but not K538R complements the recruitment of RAD52 after damage. The fold average increase of foci intensity of GFP-RAD52 at TA-KR damage sites is quantified (n = 10). (F and G) GFP-RAD52/GFP-RAD51C stably expressed in 293 cells with or without 5 Gy IR was immunoprecipitated by anti-GFP with 1 h postirradiation incubation. Detection of CSB deletions (F) or mutants (G) by anti-FLAG, HA, or myc is shown.