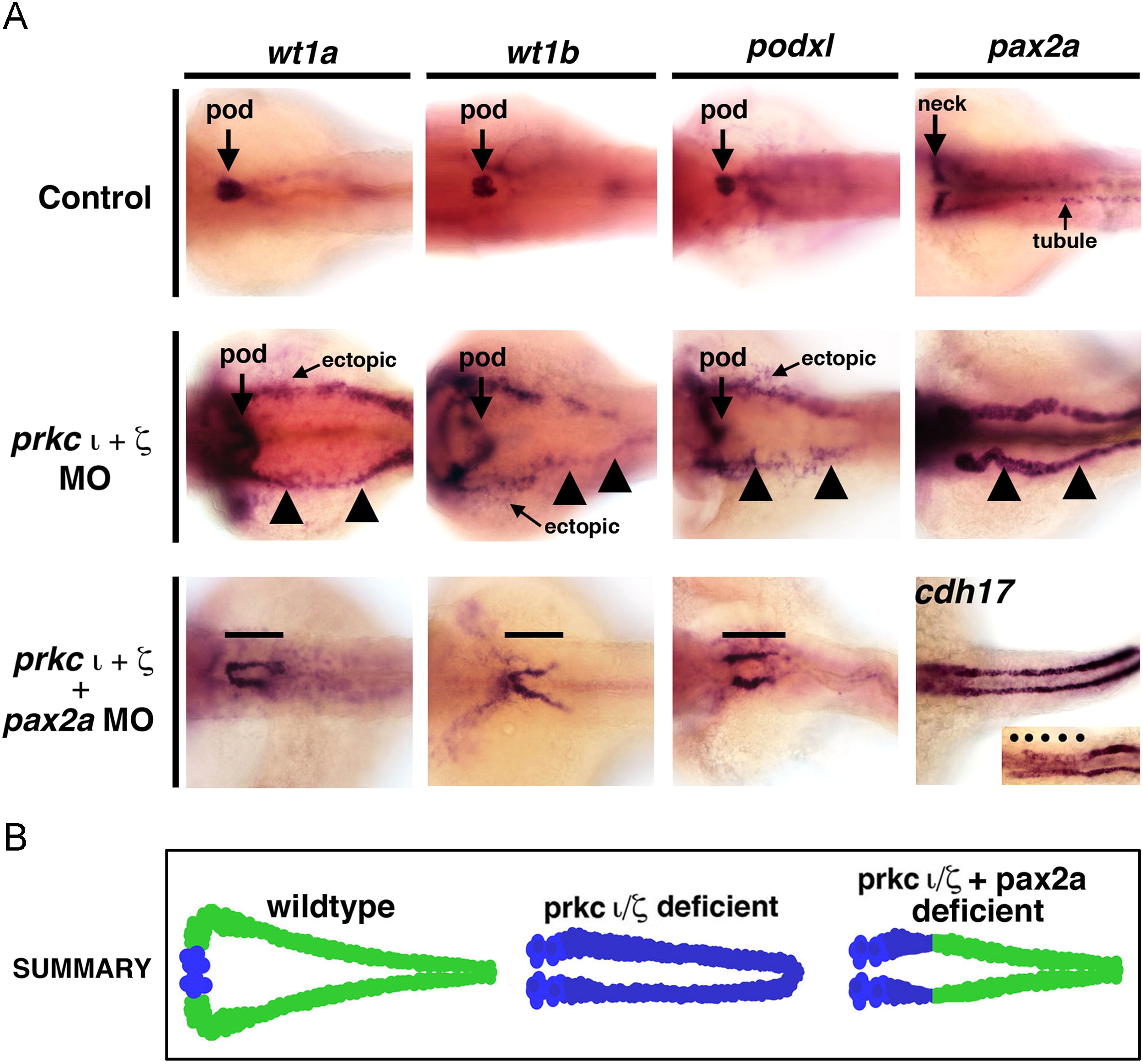
Fig. 9
Fig. 9 Ectopic expression of early developmental transcription factors in prkCI/? morphants is abrogated by concomitant knockdown of pax2a. WISH was used to assess gene expression using antisense riboprobes to detect wt1a, wt1b, podxl, pax2a or cdh17 (purple), in (A) wild-types, (B) prkCI/? morphants, or (C) prkCI/? morphants with combined pax2a knockdown. Wild-types showed restricted podocyte expression of wt1a, wt1b, and podxl, while pax2a was localized to the neck and intermittent pronephros tubule cells. prkCI/? morphants had high ectopic expression of each gene in the pronephros tubule. Knockdown of pax2a in prkCI/? morphants was associated with a short proximal pronephros domain of ectopic wt1a, wt1b, and podxl expression and low cdh17 transcript levels, while the tubule segment past this short ectopic segment domain was present and marked by a robust level of cdh17 transcripts. (D) Summary of ectopic misexpression during prkCI/? loss of function: wild-type embryos have mutually exclusive domains of podocyte versus tubule gene expression, prkCI/? morphants have ectopic misexpression of transcription factors throughout the pronephros, and pax2a knockdown represses this ectopic tubule misexpression in prkCI/? morphants, except for the neck region of the pronephros.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 396(2), Gerlach, G.F., Wingert, R.A., Zebrafish pronephros tubulogenesis and epithelial identity maintenance are reliant on the polarity proteins Prkc iota and zeta, 183-200, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.