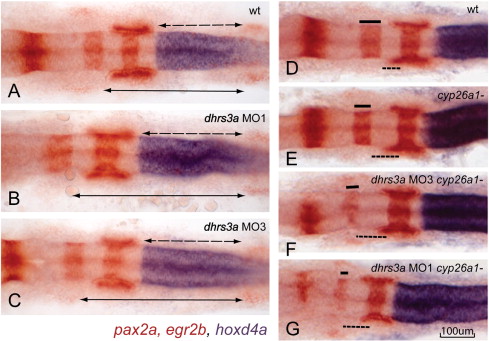
Fig. 8 Dhrs3a knockdown effects nervous system patterning. (A?C) in situ hybridization of hoxd4a (blue), pax2a (red in mid-hindbrain boundary, otic vesicles and somites) and egr2b (red in rhombomere 3 and 5) in wt (A), dhrs3a MO1 (B) and MO3 (C)-injected embryos. Dotted arrows indicate the distance from the r6/7 boundary, marked by the anterior limit of hoxd4a expression, to the second somite (indicated by the anterior limit of pax2a expression). Solid arrows indicate the distance from the r3/4 boundary to the second somite. Both distances are longer in dhrs3a knockdown embryos. (D?G) Knockdown of Dhrs3 enhances the posteriorized hindbrain phenotype of cyp26a1 mutant embryos: (D) wt; (E) cyp26a1-/gir mutant; (F, G) cyp26a1-/gir mutant injected with dhrs3a MO3 (F) or MO1 (G).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 338(1), Feng, L., Hernandez, R.E., Waxman, J.S., Yelon, D., and Moens, C.B., Dhrs3a regulates retinoic acid biosynthesis through a feedback inhibition mechanism, 1-14, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.