Fig. 1
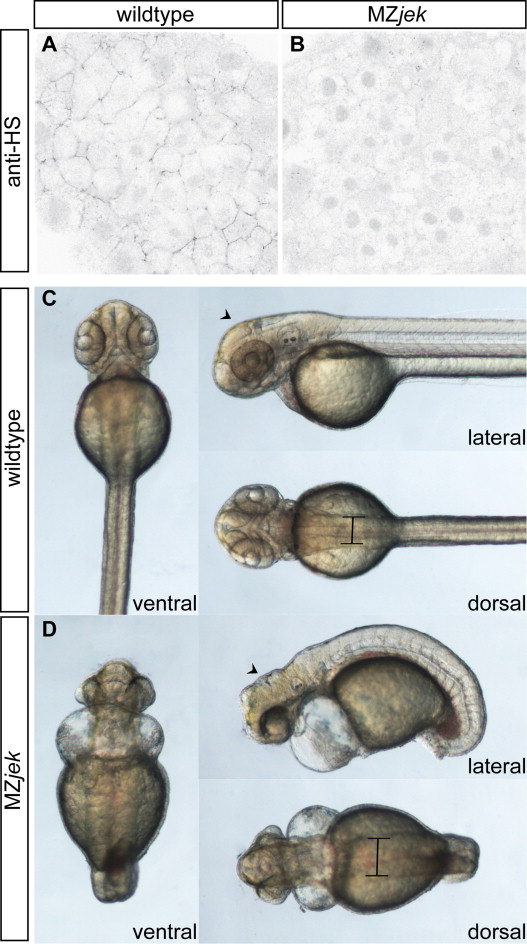
MZjek mutant embryos lack extracellular heparan sulfate proteoglycans and display multiple morphological abnormalities. (A,B) Representative confocal micrographs of anti- heparan sulfate PG staining in the animal pole of shield-staged wildtype (A) and MZjek mutant (B) embryos (N=20,20 respectively). Anti-heparan sulfate staining is clearly present in the extracellular space of wildtype embryos. In MZjek, there is an absence of HS staining, suggesting HS GAGs are not synthesized in the mutant. (C,D) Live images of 48 hpf WT (C) and MZjek mutant embryos (D) mounted for lateral, dorsal and ventral views. MZjek (D) exhibit an expanded mediolateral axis (bars), defects in axial extension, brain patterning defects (arrowheads) and disrupted heart morphogenesis.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 387(2), Superina, S., Borovina, A., and Ciruna, B., Analysis of maternal-zygotic ugdh mutants reveals divergent roles for HSPGs in vertebrate embryogenesis and provides new insight into the initiation of left-right asymmetry, 154-166, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.