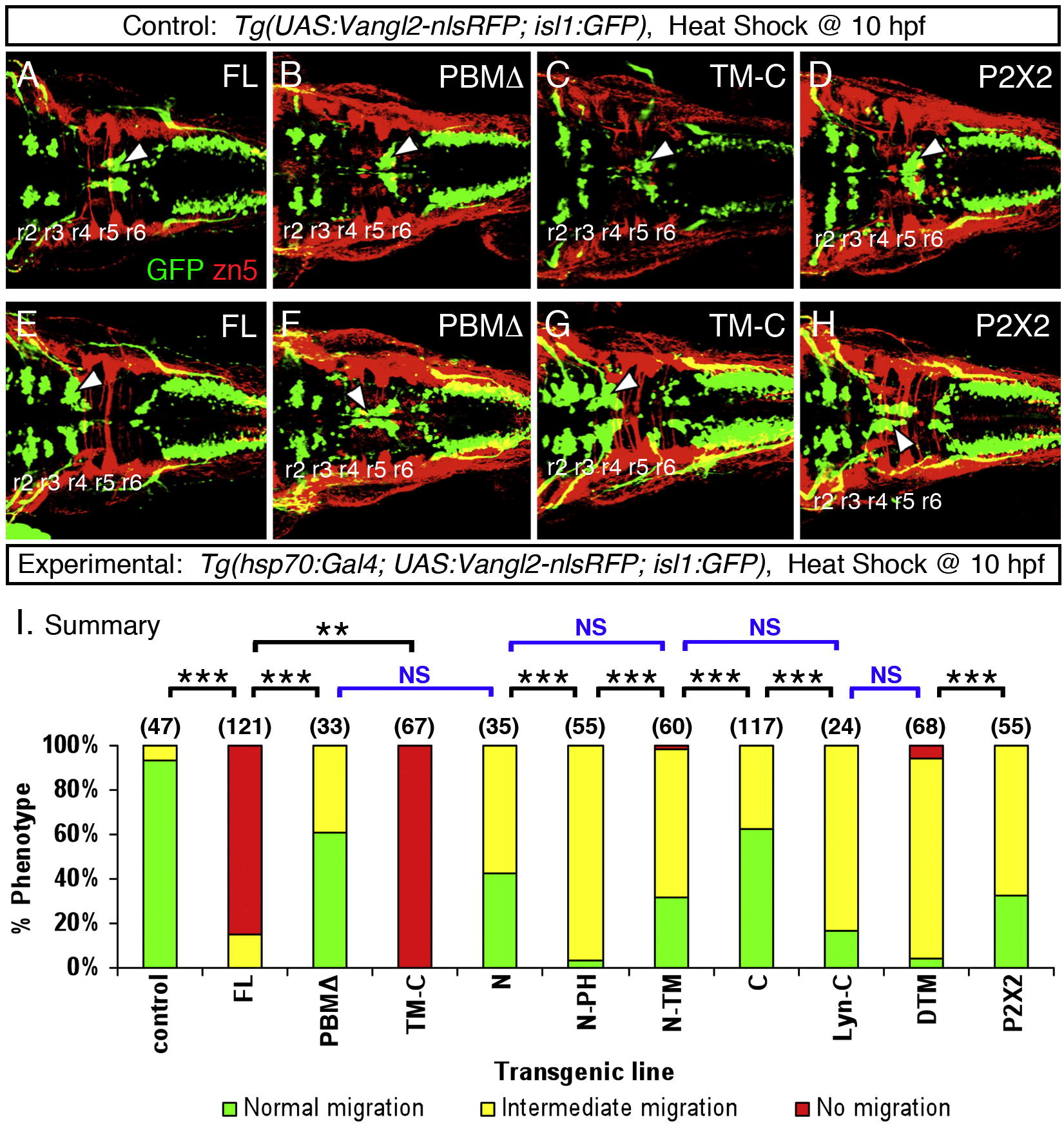
Fig. 4 Heat shock-induced overexpression of Vangl2 FL or Vangl2 TM-C strongly interferes with FBM neuron migration (A?H). Dorsal views of 48 hpf embryos processed for anti-GFP and zn5 immunohistochemistry. The upper panels (A?D) represent the control conditions for the corresponding lower panels (E?H) representing the experimental embryos expressing different Vangl2 transgenes following heat shock at 10 hpf. In control embryos (A?D), GFP-expressing FBM neurons largely undergo normal caudal migration from r4 into r6 (arrowhead). Zn5 staining (red) labels rhombomere boundaries. The trigeminal and vagal motor neurons are located in r2 and r3, and the caudal hindbrain, respectively. In experimental embryos, Vangl2 FL and Vangl2 TM-C overexpression result in failure of caudal neuronal migration (E, G), whereas a majority of FBM neurons migrates out of r4 following Vangl2 PBM? and P2X2 overexpression (F, H). However, many neurons fail to migrate into r6, a phenotype classified as intermediate migration (see panel I). Positions of the trigeminal and vagal motor neurons are not affected by these treatments. (I) Summary of effects on FBM neuron migration following heat shock-induced Vangl2 transgene expression. Number of embryos scored in parenthesis for each construct. Data pooled from 2 to 5 experiments. Some constructs (FL, TM-C) resulted in migration failure in >80% of injected embryos. FBM neurons largely migrated out of r4 for the remaining constructs, but overexpression of some (N, N-PH, N-TM, Lyn-C, DTM, P2X2) generated intermediate migration phenotypes in >50% of embryos. Significant differences p < 0.05 and p < 0.001 (Pearson Chi Square test) are indicated by (**) and (***), respectively. NS, not significant.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 131, Pan, X., Sittaramane, V., Gurung, S., and Chandrasekhar, A., Structural and temporal requirements of Wnt/PCP protein Vangl2 function for convergence and extension movements and facial branchiomotor neuron migration in zebrafish, 1-14, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.