Fig. 3
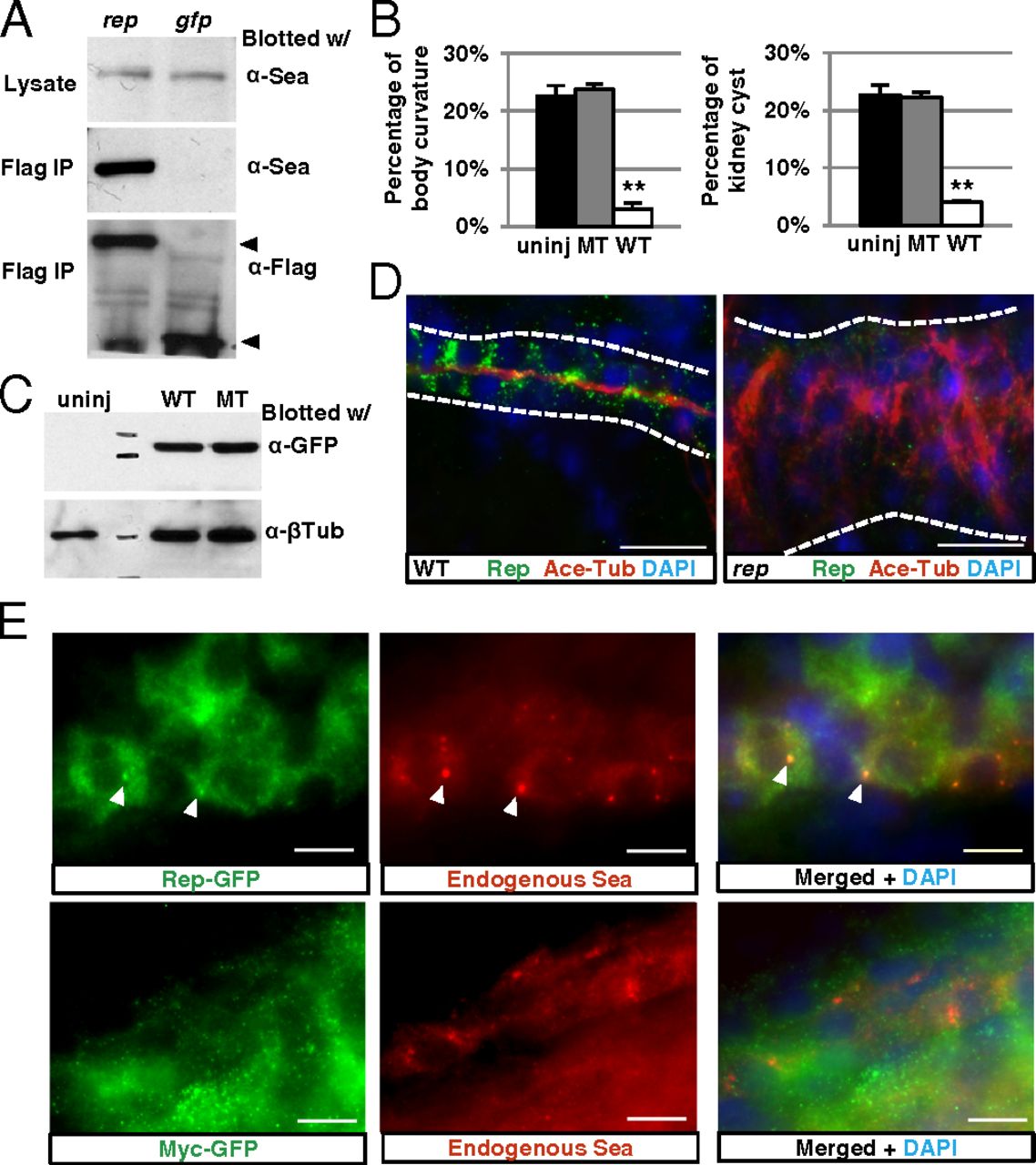
Reptin binds to and colocalizes with Lrrc6/Seahorse. (A) Anti-Flag IP brings down endogenous Lrrc6/Seahorse in lysates of 2-dpf embryos overexpressing Flag-tagged Reptin (rep), but not in embryos overexpressing Flag-tagged eGFP (gfp). Bottom arrow points to Reptin-Flag (Left) and Gfp-Flag (Right). To avoid interference from the signal of IgG light chain, the blot was cut at the bottom before exposure. (B) The percentage of body curvature (Left) and kidney cyst (Right) in embryos from seahorsehi3308+/- crosses uninjected (uninj), injected with wild-type seahorse mRNA (WT), and mutant seahorse mRNA encoding full-length Seahorse with the amino acids 392–396 alanine substitution (MT). Data are represented as mean + SD, from three replicates, **P < 0.01. (C) Western blot on whole embryo lysate of embryos from seahorsehi3308+/- crosses unjected (uninj), injected with GFP-tagged wild-type seahorse mRNA (WT), or GFP-tagged mutant seahorse mRNA as in B (MT). (D) Immunostaining of the pronephric duct (white line) in 4-dpf wild type (WT) and reptinhi2394 mutants (rep). Cilia are labeled with antiacetylated tubulin (Ace-Tub) in red, and Reptin is labeled with anti-Reptin (Rep) in green. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (E) Immunostaining of the pronephric duct in 1-dpf embryo showing overexpressed Reptin-eGFP (Upper, green) and endogenous Seahorse (Sea, red). Overexpressed Myc-eGFP is shown (Lower) as a negative control. Arrowheads point to puncta positive for both Reptin eGFP and Seahorse. (Scale bar, 10 μm.)