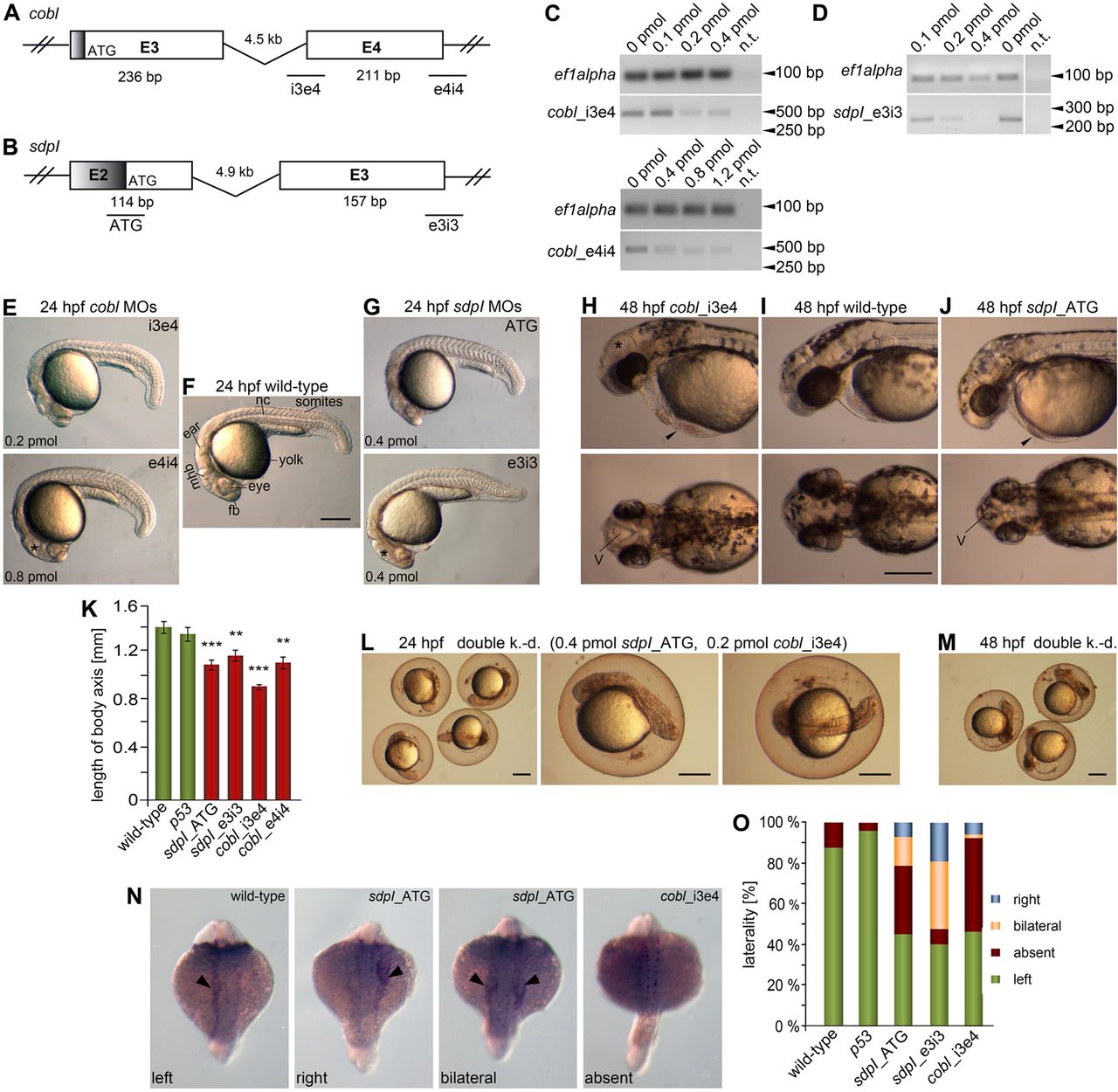
Fig. 2 MO-mediated knock-down of cobl and syndapin I leads to similar defects in brain, body and motile cilia-driven body laterality development. (A,B) Position of MOs for cobl (A) and syndapin I (B) on the respective genes (ORF in white; UTRs in grey). MO cobl_i3e4 and MO cobl_e4i4 prevent correct splicing (A). For syndapin I, an ATG-targeting and a splice-preventing MO (sdpI_e3i3) were designed (B). (C,D) Knock-down of cobl (C) and syndapin I (D) using increasing amounts of the splice-preventing MOs cobl_i3e4, cobl_e4i4 and sdpI_e3i3 validated via RT-PCR using whole-body mRNA at 24h post injection and at the 16 somite stage for MO cobl_i3e4; ef1alpha amplification was used for normalization. n.t., no template. (E?J) Cobl- and syndapin I-morphant embryos show similar phenotypes at 24hpf (E,G) and 48hpf (H,J). Note the shortened anterior?posterior body axes, heart (arrowheads) and brain with oedema (asterisks) and increased ventricle sizes (examples marked), and smaller heads and eyes. (L,M) Double knock-down of cobl and syndapin I leads to dramatically enhanced phenotypes (L, 24hpf; M, 48hpf) (embryos not dechorionated). Scale bars: 250μm. fb, forebrain; mhb, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; nc, notochord; v, ventricle. (K) Quantitative analysis of lengths of the body axis at 24hpf. Wild-type, n = 18; MO p53, n = 9; MO sdpI_ATG, n = 12; MO sdpI_e3i3, n = 15; MO cobl_i3e4, n = 20; MO cobl_e4i4, n = 7. Statistical analyses, ANOVA with Tukey?s test versus wild-type. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (N,O) Cobl and syndapin I morphants display impaired laterality formation (in situ hybridization of pitx2 (arrowheads); exemplary images underscoring quantification of pitx2 distribution in wild-type, control-injected (p53) and morphant embryos at 20?22 somite stages). Wild-type, n = 174; MO p53, n = 47; MO sdpI_ATG, n = 42; MO sdpI_e3i3, n = 42; MO cobl_i3e4, n = 67.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ J. Cell Sci.