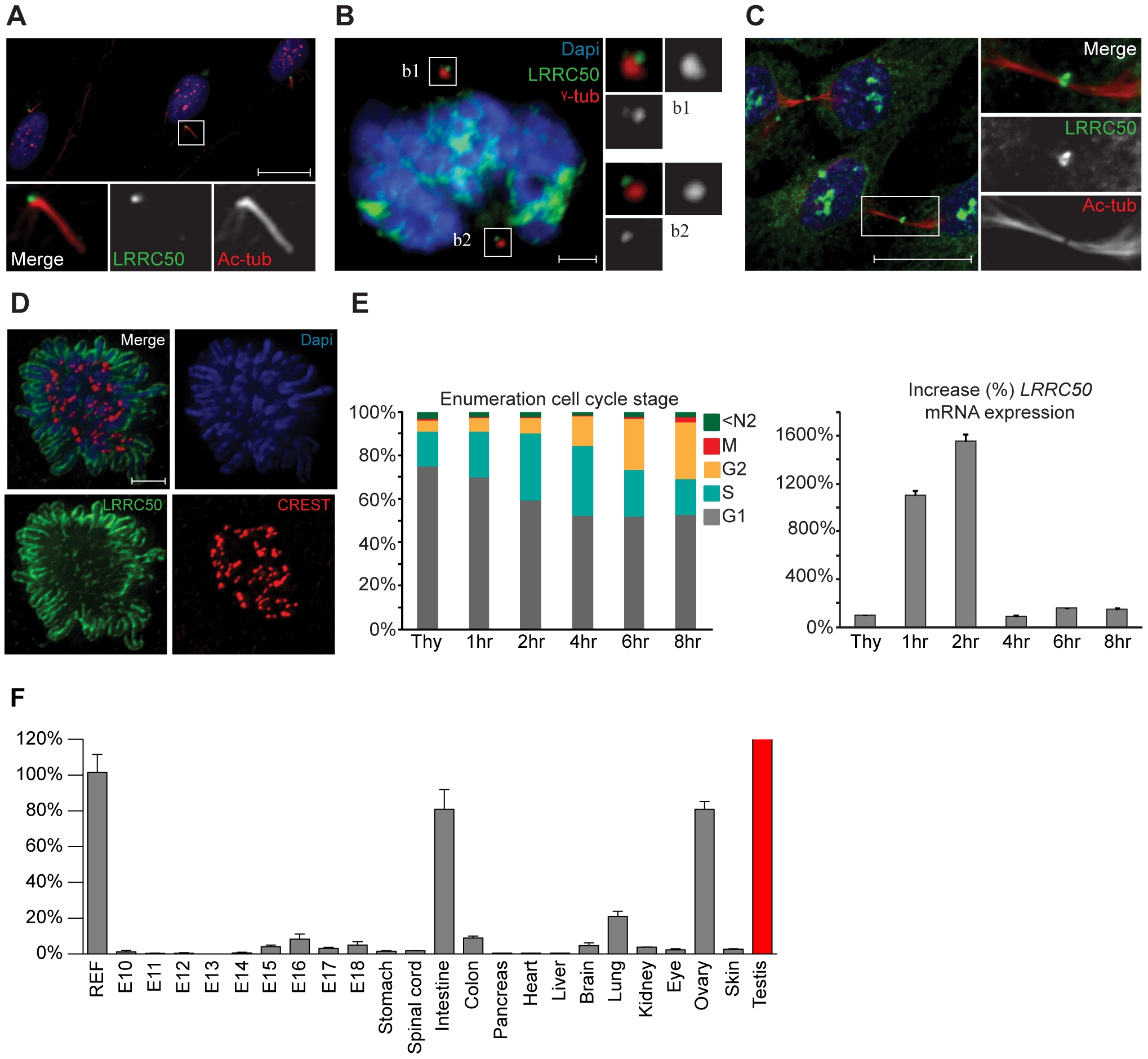
Fig. 5
Localization and expression of LRRC50.
LRRC50 antibody ab75163 (reproducible with alternative LRRC50 antibodies) shows a dynamic, cell cycle dependent, distribution in RPE-hTERT cells (representative for other tested mammalian cell lines). Panels represent LRRC50 (green) at various stages, counterstained with DAPI (blue) and acetylated-α-tubulin (Ac-tub, red). Optical sections in A-C are 3 μm. (A) In ciliated serum-starved cells, LRRC50 localizes to the peripheral centrosome/basal body region dorsal of the axoneme (red). Scale bar 10 μm. (B) In mitotic cells, LRRC50 remains associated with the duplicated centrosomes, as indicated with γ-tubulin (red). Inserts b1,2 demonstrate a peri-centrosomal localisation. Scale bar 2 μm. (C) Temporal localization to the midbody in cytokinesis. Scale bar 10 μm. (D) During mitosis LRRC50 dynamically associates with condensed chromosomes (extensively described in Figure S5B). Counterstain CREST (red) marks kinetochores. Image is a maximum intensity projection of deconvoluted stacks. Scale bar 2 μm. (E) Dynamic LRRC50 mRNA expression (correlating with dynamic localization) with error bars as standard deviation. T47D cells synchronized at the G1/S transition with thymidine show a strong LRRC50 transcript up-regulation upon release, specifically in the cell population entering early S-phase (see also Figure S6A). Intriguingly; although the protein remains stable during mitosis (shown in D) the transcript is rapidly down-regulated, and restored to basal levels. (F) Expression profiling of LRRC50 mRNA expression with error bars of standard deviation in a library of mouse cDNA tissues normalized to full mouse reference pool. Testis expression shown in red as the expression level (>26.000%) strongly exceeds the normalized value.