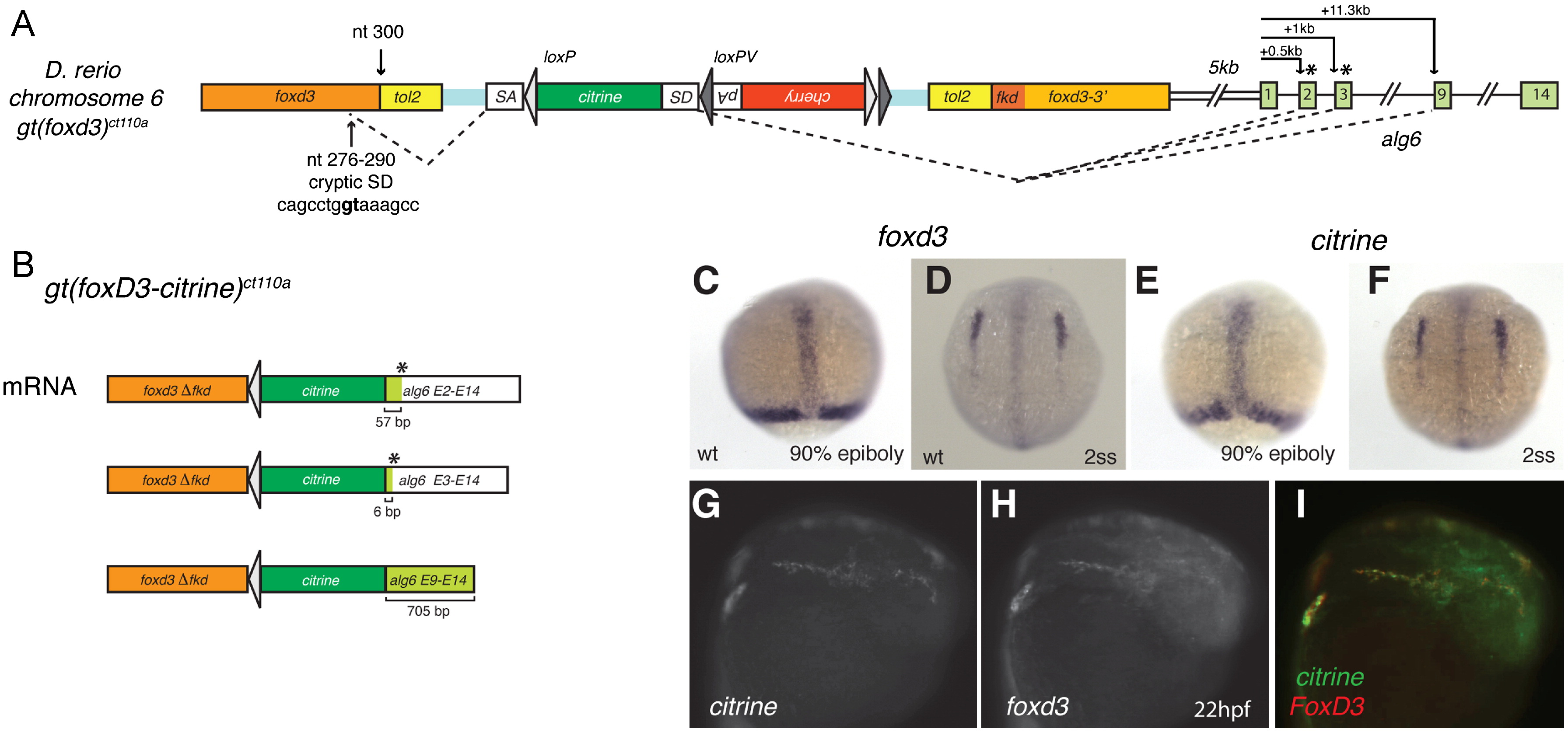
Fig. 2 Expression of citrine in ct110a reflects endogenous expression of foxd3. (A) Schematic diagram of genomic FlipTrap integration in the ct110a line. Integration of the FlipTrap construct occurred within the coding region of foxd3, in chromosome 6. Splice acceptor site (SA) of the citrine internal exon recognizes a cryptic splice donor site within foxd3 sequence (nucleotides 276?290 of foxd3 coding sequence). The splice donor site (SD) of citrine reacts with acceptor sites of alg6. The citrine exon splices with exons 3 or 9 of alg6, respectively situated at +1 kb or +11.3 kb downstream from the alg6 start site in the genomic sequence. (B) Splicing events produce a chimeric Citrine-fusion protein, which encodes the N-terminal portion of FoxD3 (FoxD3??Fkd) and an Alg6 tail. Splicing of citrine with exon 2 or 3 of alg6 results in a short Alg6 tail (19 or 2 aminoacids, respectively), caused by a premature stop signal (*) generated by a frame shift. Alternative splicing with exon 9 does not affect the coding frame. (C?I) Expression of citrine recapitulates foxd3 expression in the Gt(foxd3-citrine)ct110a line. Whole mount in situ hybridization to foxd3 (C and D) and citrine (E and F). (C) Early expression of foxd3 in the prechordal plate and blastoderm margin of zebrafish embryos in late gastrula. (D) foxd3 expression by neural crest cells initiates during early somitogenesis, as bilateral fields in the anterior neural plate border. (E and F) Distribution of citrine transcripts in Gt(foxd3-citrine)ct110a embryos corresponds to endogenous expression of foxd3. (G?I) citrine mRNA co-localizes with foxd3 endogenous expression in neural crest cells. Double fluorescent whole mount in situ hybridization to citrine and foxd3 in Gt(foxd3-citrine)ct110a embryos at 22 hpf.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 374(1), Hochgreb-Hägele, T., and Bronner, M.E., A novel FoxD3 gene trap line reveals neural crest precursor movement and a role for FoxD3 in their specification, 1-11, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.