Fig. 4
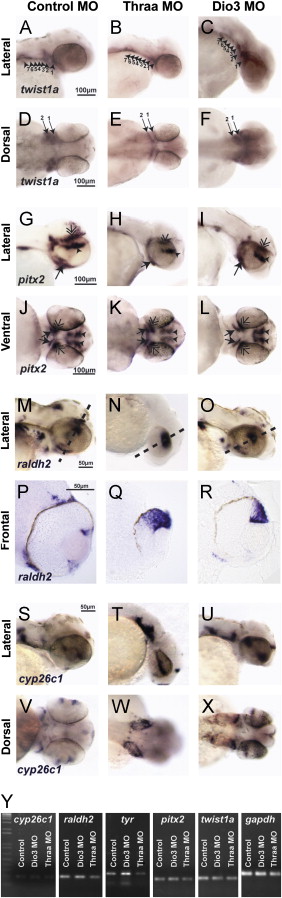
Fig. 4 TH regulates expression of twist1a and pitx2. 48 hpf expression of twist1a by in situ hybridization demonstrated decreased expression in Thraa MO knockdowns (B, E) which was expressed in pharyngeal arches (arrowheads) in controls (A, D). Increased TH (via MO knockdown of Dio3) demonstrated increased expression of twist1a within pharyngeal arches (C, F, arrowheads). In situ hybridization for pitx2 demonstrated markedly decreased expression in periocuar mesenchyme of Thraa MO knockdowns (H, K, double arrowheads) and slightly decreased expression in POM of Dio3 (I, L, double arrowheads) MO knockdown. Pitx2 was normally expression in the jaw (arrows), POM (double arrowheads), optic nerve (large arrowheads) and pituitary (small arrowheads) in control embryos (G, J). In situ hybridization demonstrated in control embryos that raldh2 was expressed in ventral and dorsal retina, jaw, and POM at 48 hpf (M, P). In Thraa MO knockdowns, raldh2 was only expressed in the dorsal retina at 48 hpf (N, Q). MO knockdown of Dio3 decreased expression of raldh2 in pharyngeal arches and POM (O, R). In situ hybridization in control embryos demonstrated expression of cyp26c1 in a demarcating line between dorsal and ventral retina, hindbrain, and otic vesicle 48 hpf (S, V). MO knockdown of Thraa (T, W) and Dio3 (U, X) increased expression of cyp26c1 in the retina, hindbrain, and otic vesicle. Scale bar=50 Ám. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of RNA (Y) derived from whole 36 hpf control, Dio3 MO, or Thraa MO demonstrated no difference in expression of cyp26c1, pitx2, and twist1a. RT-PCR demonstrated decreased overall expression of raldh2 and tyrosinase (tyr) in Thraa MO compared to control. Dio3 MO knockdown showed increased expression of tyr. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR used Gapdh and S18 (data not shown) as internal controls.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 373(2), Bohnsack, B.L., and Kahana, A., Thyroid hormone and retinoic acid interact to regulate zebrafish craniofacial neural crest development, 300-309, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.