Fig. 1
Fig. 1
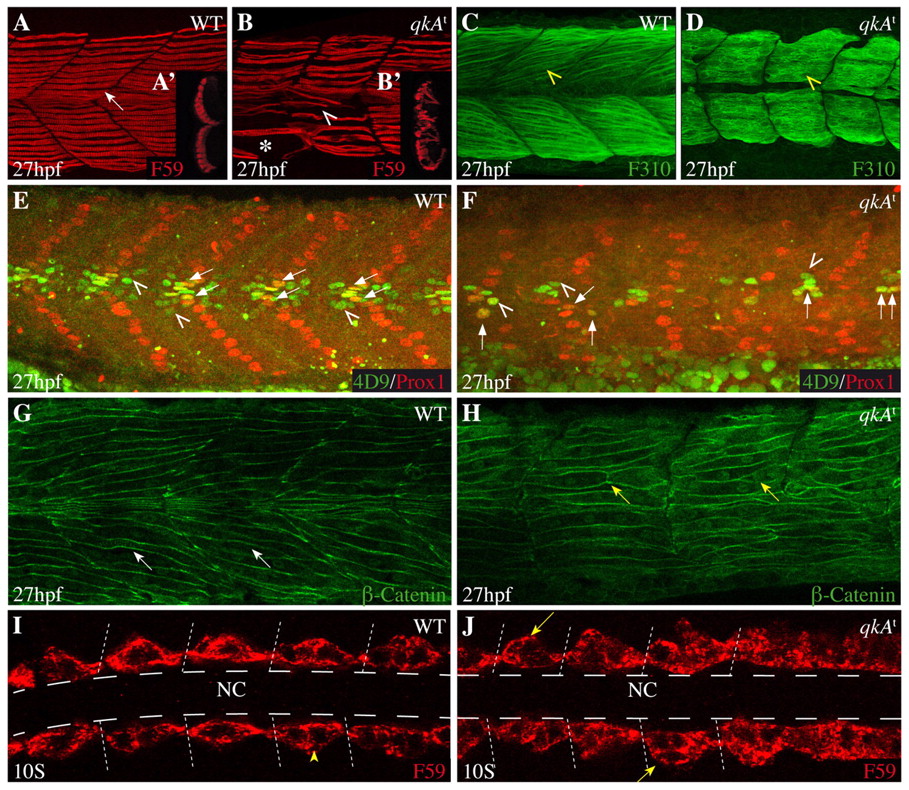
Requirement for qkA during somite development. (A-H) Lateral views from 27-hpf zebrafish embryos of the indicated genotypes (upper right) immunostained with the indicated markers (lower right) and analyzed by confocal imaging. Anterior is to the left. (A-B2) Slow muscle cells labeled by F59 (arrow) are disorganized in qkAt homozygotes (arrowhead), are less numerous, exhibit gaps (asterisk) and invade the fast muscle domain (see optical transverse sections in insets A2,B2). (C,D) Fast muscle fibers (yellow arrowhead) appear immature in qkAt homozygotes, with predominantly cytosolic staining and imprecise contours. (E,F) Muscle subpopulations are reduced in qkAt. Embryos were stained for Prox1 [slow muscle cells, including muscle pioneers (MPs)] and Engrailed [MPs (arrows) and medial fast fibers (MFFs; arrowheads) by 4D9 antibody]. Note the reduction in all these cell types in the qkAt homozygotes. (G,H) qkA is required for fast myotube formation. β-catenin staining reveals a large number of short mononucleated cells (yellow versus white arrows) in the fast muscle domain, indicating retarded fusion. (I,J) Early requirement for qkA in slow muscle development. Ten-somite stage embryos stained for slow muscle, dorsal view. At this stage, adaxial cells abut the notochord in wild type (WT) (arrowhead), whereas mutant somites often exhibit several mislocated cells (arrows). Dashed lines indicate the position of the notochord. NC, notochord.