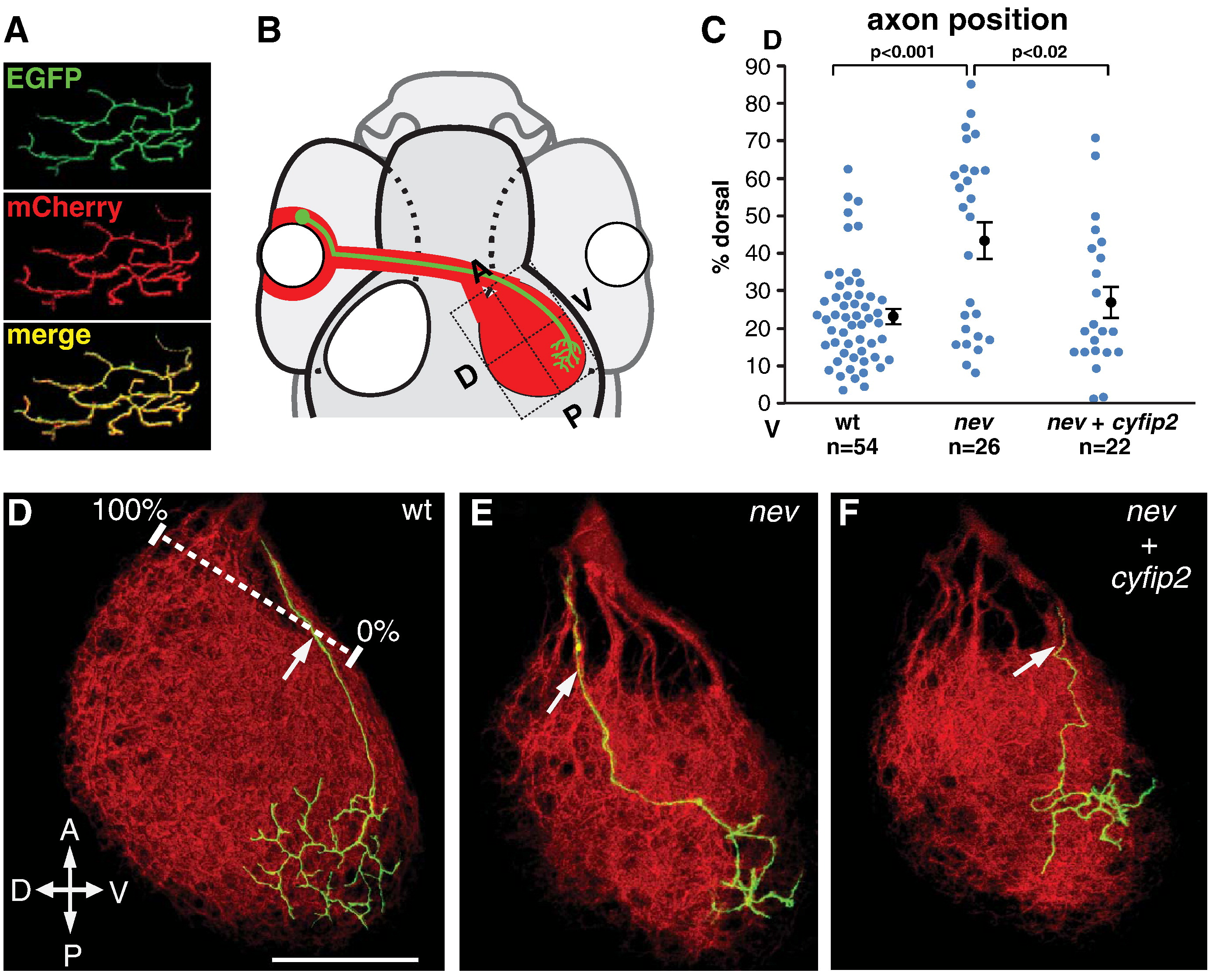
Fig. 8 cyfip2 acts cell autonomously in dorsonasal RGC axon sorting in the optic tract. (A) Co-electroporation yields consistent co-labeling with EGFP and mCherry. (B) Diagram of rescue experiments: electroporated dorsonasal RGCs project to the posteroventral quadrant of the tectum. (C) Quantification of D-V sorting of dorsonasal axons in the optic tract as they enter the right optic tectum, relative to the ventralmost (0%) and dorsalmost (100%) fascicles (white ruler in D). A subset of nev axons missorts into the dorsal brachium; electroporation with cyfip2 yields significant rescue. Error bars show mean ± SEM. (D?F) Confocal projections of single dorsonasal axons (GAP43-GFP, green) in the tectal neuropil (mCherryCAAX, red) at 5 dpf. (D) WT axons enter the tectum ventrally. (E) nev axons often enter dorsally. (F) cyfip2-co-electroporated nev axons are rescued and enter ventrally. Scale bar, 50 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 344(2), Pittman, A.J., Gaynes, J.A., and Chien, C.B., nev (cyfip2) Is required for retinal lamination and axon guidance in the zebrafish retinotectal system, 784-794, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.