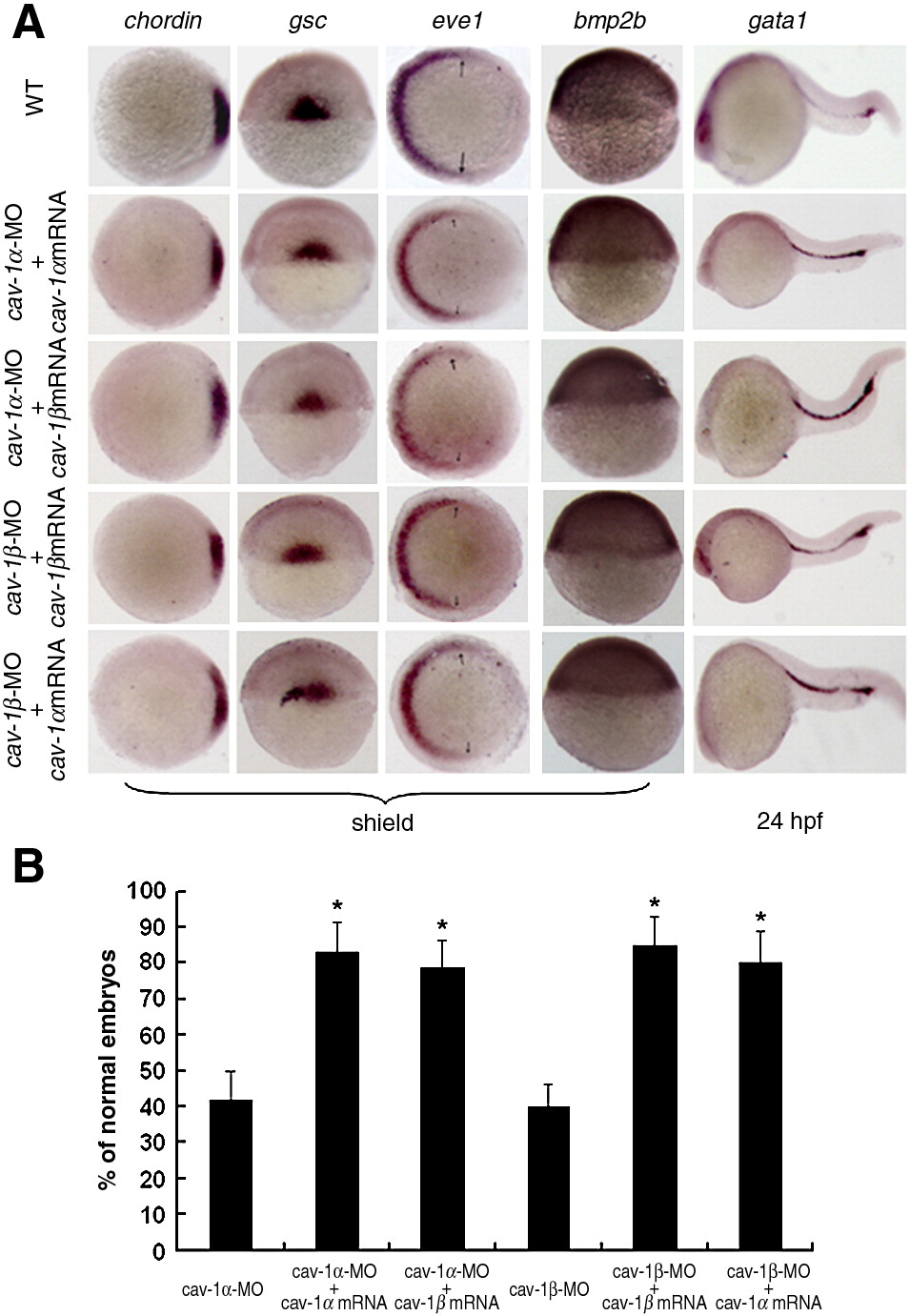
Fig. 3
Fig. 3 Abnormal phenotypes of Cav-1 knockdown embryos can be rescued by its capped mRNAs. (A) Abnormal expression patterns of dorsoventral marker genes caused by injection of Cav-1-MO can be rescued by its corresponding or another isoform mRNAs. Developmental stages are shown at the bottom. Animal pole views of embryos at shield stage with the dorsal toward the right for chordin and eve1 and arrows point to the margins of expressed eve1. Lateral views of embryos at shield stage with the dorsal toward the right for bmp2b. Dorsal views of embryos at shield stage with the animal pole toward the top for gsc. Lateral views of embryos at 24 hpf with the anterior to the left for gata1. (B) Percentage of normal embryos injected with 5 ng cav-1α-MO, 5 ng cav-1α-MO plus 300 pg cav-1α mRNA, 5 ng cav-1α-MO plus 300 pg cav-1β mRNA, 5 ng cav-1β-MO, 5 ng cav-1β-MO plus 300 pg cav-1β mRNA, 5 ng cav-1β-MO plus 300 pg cav-1α mRNA. Data represent mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. *indicates p < 0.05 vs. cav-1α-MO or cav-1β-MO.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 344(1), Mo, S., Wang, L., Li, Q., Li, J., Li, Y., Thannickal, V.J., and Cui. Z., Caveolin-1 regulates dorsoventral patterning through direct interaction with beta-catenin in zebrafish, 210-223, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.