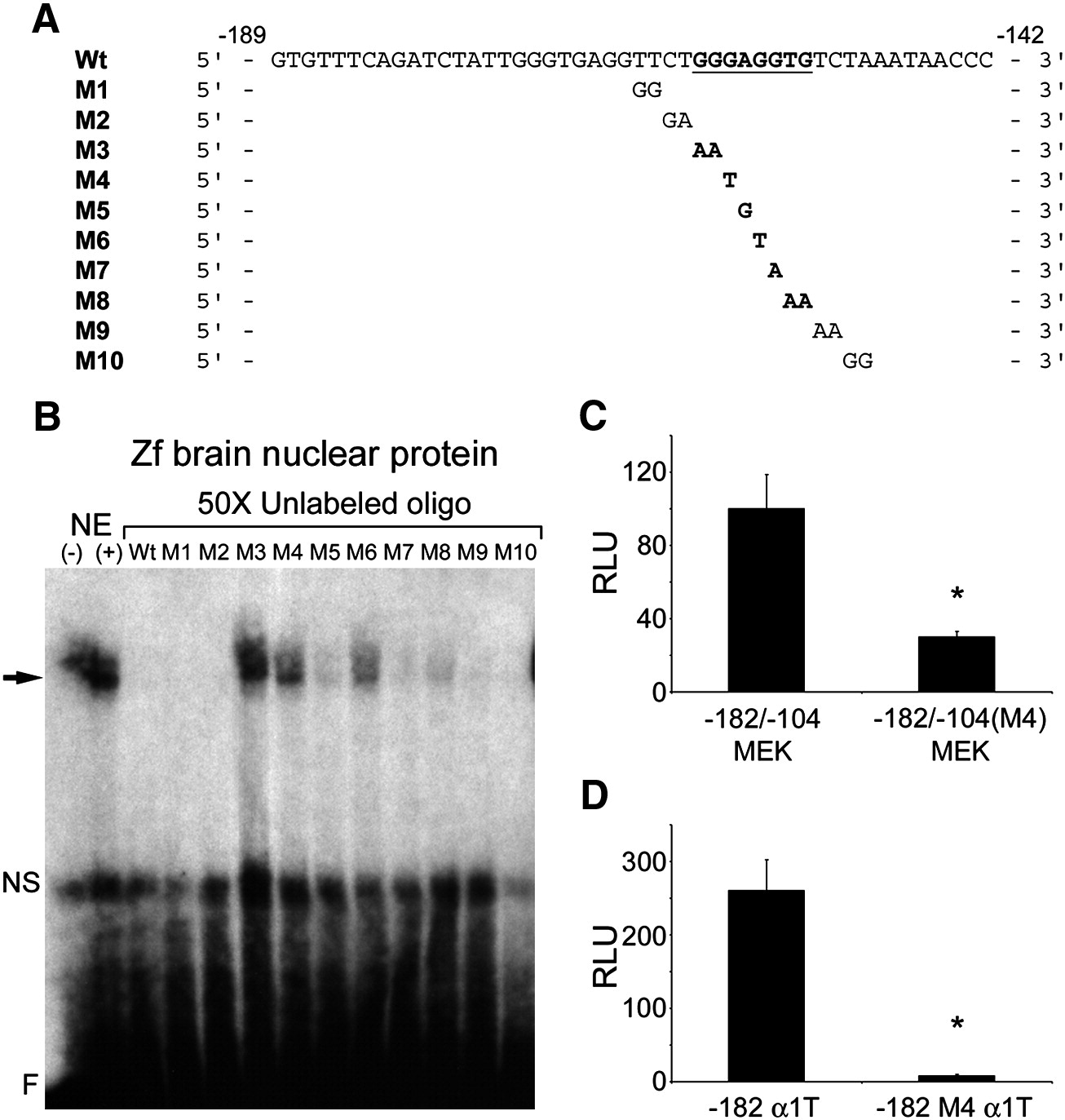
Fig. 6 Mutation analysis of the - 182/-104 tuba1a enhancer identifies a G/C-rich sequence that is necessary for nuclear protein binding and enhancer activity. (A) DNA sequences of the oligonucleotides used for mapping the protein binding site in (B). Wt, is the wildtype sequence with the G/C-rich sequence found to be necessary for protein binding typed in bold and underlined. M1?M10, show the basepair changes made in the Wt oligonucleotides for mapping the protein binding enhancer element. (B) EMSA demonstrates that a G/C-rich sequence is necessary for binding nuclear proteins from zebrafish brains. Nuclear protein extract was mixed with radiolabeled Wt oligonucleotides with and without 50x excess of unlabelled mutant oligonucleotides, M1?M10. Specific binding is indicated by a black arrow, nonspecific binding (NS), and free probe (F). Note mutant oligonucleotide competitors M3?M8 partially or completely failed to compete for binding, indicating that these nucleotides are critical for protein binding to the - 182/-104 tuba1a enhancer. (C) A single basepair mutation in the tuba1a enhancer′s G/C-rich sequence reduces enhancer activity in PC12 cells. PC12 cells were transfected with - 182/-104MEK (see Fig. 5B) or - 182/-104(M4)MEK (harbors the - 182/-104 G/C-rich enhancer with the single basepair mutation present in the M4 oligonucleotide, shown in (A), in front of the MEK promoter) along with CMV-CAT for normalization. (D) A single basepair mutation in the G/C-rich protein binding site of the - 182 tuba1a reporter (- 182 α1T in Fig. 5A) reduces promoter activity in PC12 cells. PC12 cells were transfected with - 182 α1T or - 182 M4 α1T (harbors the - 182 α1T sequence with the M4 mutation present in the G/C-rich protein binding site). (C and D) Two days post-transfection cells were assayed for luciferase and CAT activities. Luciferase activity was normalized to CAT activity and reported as relative light units (RLU). Note a single nucleotide substitution in the α1T (tuba1a) promoter′s G/C-rich element decreases enhancer activity. Values are means +/- SEM (*p < 0.01, t-test).
Reprinted from Molecular and cellular neurosciences, 43(4), Veldman, M.B., Bemben, M.A., and Goldman, D., Tuba1a gene expression is regulated by KLF6/7 and is necessary for CNS development and regeneration in zebrafish, 370-383, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell Neurosci.