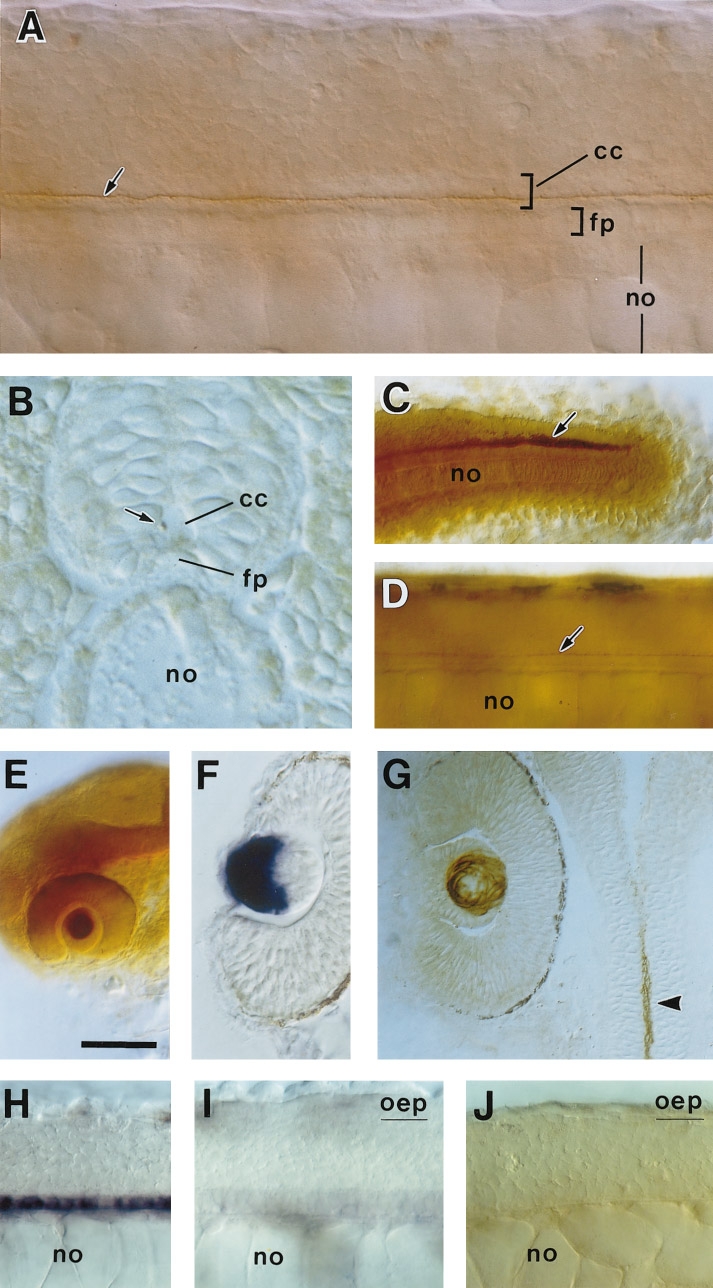
Fig. 7 Expression of F-spondin2 protein. The anti-F-spondin2 antibody Ab-spo2-1 was used for staining. (A) Lateral view of a 26-h embryo. (B) Cross section of a 26-h embryo. (C) Tail region of a 26-h embryo. Lateral view. (D) Lateral view of a 36-h embryo. Arrows in (A–D) indicate F-spondin2 immunoreactivity in the putative Reissner’s fiber. (E) Head region of a 28-h embryo. Lateral view. The lens in the eye is specifically labeled. (F) Horizontal section of the eye of a 28-h embryo stained for F-spondin2 mRNA by in situ hybridization. Epithelial layer of the lens is labeled. (G) Horizontal section of the eye of a 28-h embryo stained with the anti-F-spondin2 antibody. In contrast to the pattern of mRNA expression, F-spondin2 immunoreactivity is located in the fiber layer of the lens. An arrowhead shows the signal in the central canal. (H and I) Lateral views of 28-h wild-type (H) and oep homozygous (I) embryos stained for F-spondin2 mRNA by in situ hybridization. In the oep mutant (I), expression of F-spondin2 in the midline cells of the spinal cord is extensively reduced. (J) Lateral view of a 28-h oep homozygous embryo stained with the anti-F-spondin2 antibody. The thread-like immunoreactivity is absent. cc, central canal; fp, floor plate; no, notochord. Scale bar, 25 μm in A; 15 μm in B; 50 μm in C, D, F, and G; 100 μm in E; and 37 μm in H–J.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 192, Higashijima, S., Nose, A., Eguchi, G., Hotta, Y., and Okamoto, H., Mindin/F-spondin family: novel ECM proteins expressed in the zebrafish embryonic axis, 211-227, Copyright (1997) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.