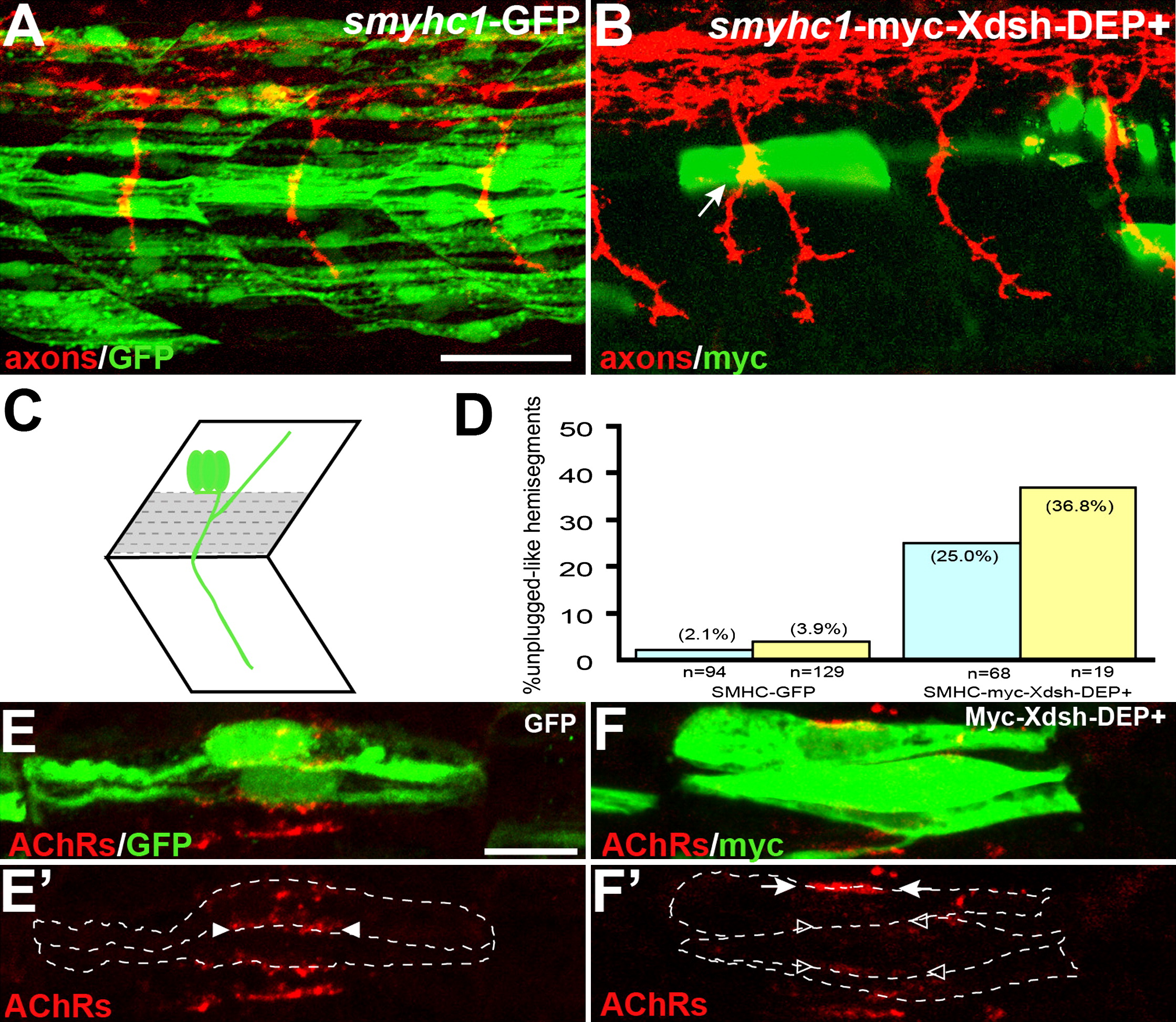
Fig. 5 Inhibition of the Noncanonical Dsh Pathway in Adaxial Fibers
(A) Stochastic expression of Tg(smyhc1:GFP) in adaxial muscle (green) does not affect motor axons (red).
(B) Expression of Tg(smyhc1:myc-XDsh-DEP+) (green) in adaxial fibers dorsal to the choice point causes unplugged-like pathfinding defects (arrow).
(C) Location of the dorsal six or seven adaxial cells (in gray) used for scoring.
(D) Analysis of axonal phenotypes. n, hemisegments; blue, hemisegments with two adaxial cells expressing the transgene; yellow, hemisegments with three or more adaxial cells expressing the transgene.
(E?F′) Confocal images of adjacent adaxial muscle pioneers expressing the smyhc1-GFP or smyhc1-myc-Xdsh-DEP+ transgene. Only AChR clusters between two adjacent transgene-positive adaxial cells were analyzed (outlined by dashed lines). Tg(smyhc1:GFP) expressing adaxial cells form AChR clusters (arrowheads in [E′]), while Tg(smyhc1:myc-XDsh-DEP+ expression disrupts AChR clusters between transgene expressing cells ([F′], open arrowhead); note that this does not affect adjacent, nontransgenic cells that formed normal AChR clusters ([F′], arrows). For each transgene, four embryos with GFP or Myc-Dsh-DEP+ positive adaxial cells were analyzed. Prepatterned clusters were reduced in all Myc-Dsh-DEP+ expressing embryos.
Scale bars: (A) 50 μm, (E) 10 μm.