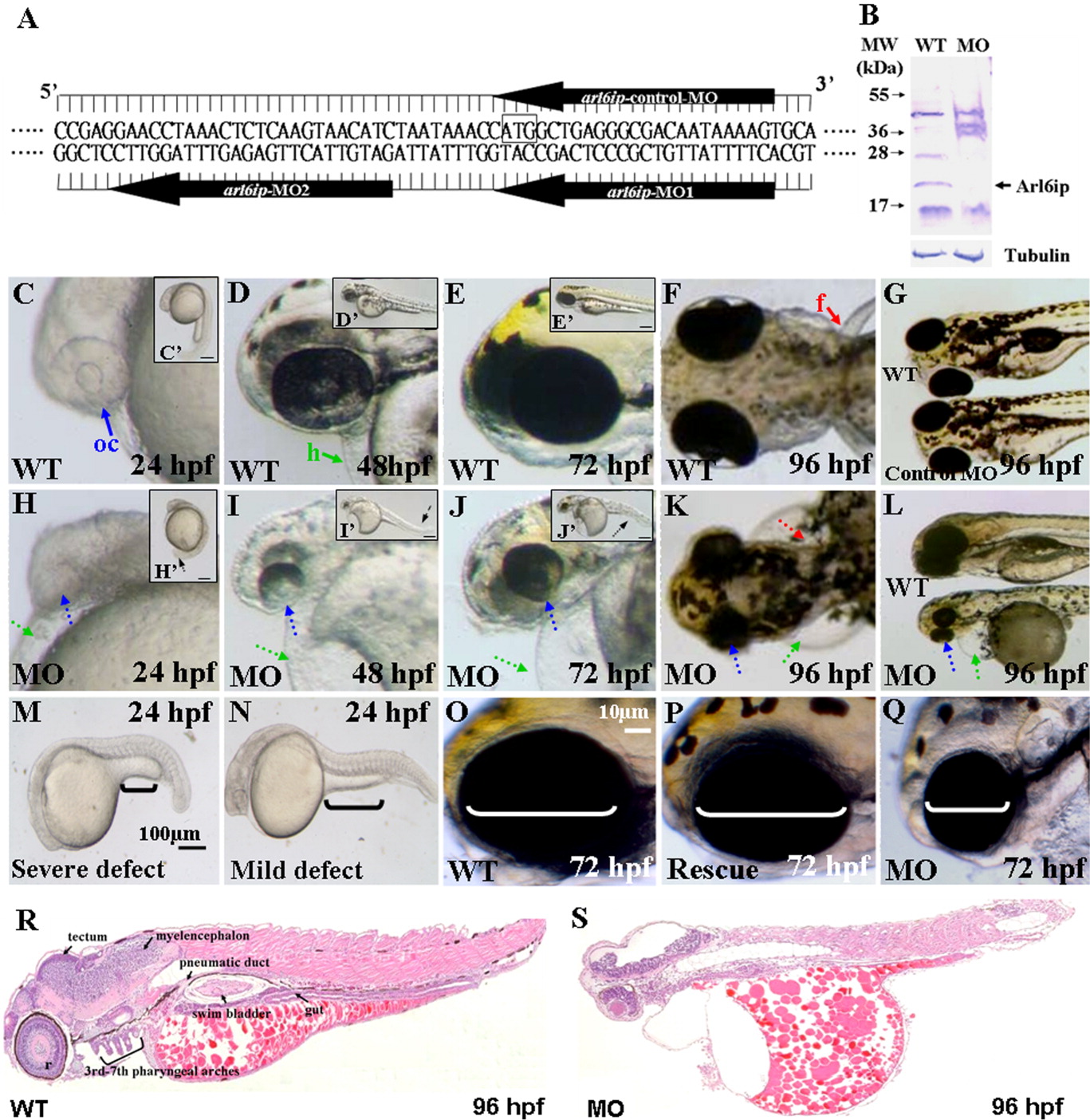
Fig. 2 A: Nucleotide sequences of the designed arl6ip-morpholino (MO). The arl6ip-MO1 targets the coding region of arl6ip mRNA, and arl6ip-MO2 targets the 5′-untranslated region. The arl6ip-control-MO served as a negative control MO, which was an inverted MO sequence of arl6ip-MO1. Square box, Arl6ip translation start site. B: Western blot analysis of total proteins extracted from the wild-type (WT) and the arl6ip-MO1-injected (MO) embryos, with β-Tubulin used as a control. The endogenous Arl6ip (arrow) from the arl6ip-morphants was completely absent. C-N: Phenotypic defects in the arl6ip-MO1-injected embryos were observed at the stages indicated. They were microphthalmia (small eyes; dotted blue arrow), pericardial edema (dotted green arrow), flat head, deformed trunk (dotted black arrow in H′-J′), pigment pattern disorder and pectoral fin defect (dotted red arrow). Black brackets indicate the extended yolk length by which we identified the different defect grades (M,N). Scale bar = 100 μm in M,N. oc, optic cup (solid blue arrow); h, heart (solid green arrow); f, fin (solid red arrow) were indicated in wild-type embryos. Scale bar = 10 μm in C′-E′,H′-J′,O-Q. The defective arl6ip-morphants (Q) were partially rescued to develop the wild-type-like phenotype (P) after co-injecting the synthetic arl6ip-mRNA with arl6ip-MO2. The white brackets indicate the eye dimensions. The histological sections were examined for the wild-type embryos and the arl6ip-morphants at 96 hpf after hematoxylin-eosin staining (R,S). Compared to the tissue morphology of wild-type embryos, arl6ip-morphants displayed many abnormalities of tissue development, including retina, tectum, myelencephalon, 3rd-7th pharyngeal arches, pneumatic duct, swim bladder, and gut.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.