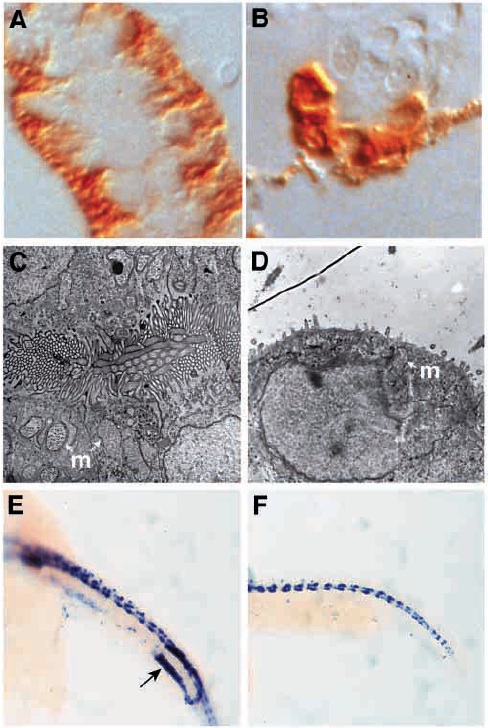
Fig. 6 Fig. 6. noi mutants show defects in pronephric duct epithelial differentiation and cloaca development. (A,C,E) Wild-type and (B,D,F) noi- embryos stained with a-6F mAb at 3 dpf (A,B) and electron micrographs of pronephric duct epithelia from 2 dpf embryos (C,D). (A) In wild-type pronephric tubule and duct, mAb a- 6F staining is basolateral reflecting the basolateral subcellular localization of Na+/K+ ATPase a-subunit. (B) In noi mutants, mAb a-6F staining is diffuse throughout the duct cells with mAb a-6F positive cells sitting adjacent to duct cells showing no mAb a-6F reactivity. Some endogenous pigmentation is seen in B and is not HRP reaction product. Electron micrograph of wild-type pronephric duct epithelia shows an abundance of microvilli and cilia packed densely in the lumen. Mitochondria (m) are excluded from the apical terminal web. In noi-, the pronephric duct lumen is greatly distended and epithelia lack a apical brush border seen in D as a huge reduction in apical microvilli. Some ciliated cells are still present. Apically localized mitochrondria (m) are seen. Cloaca development is abnormal in noi mutants. (E,F) In situ hybridization with ret1 antisense probe at 22 hpf. ret1 is expressed in a posterior domain of the pronephric duct during cloaca development (arrow in E). Ductspecific expression of ret1 is absent in noi? even though CNS expression remains unaffected (F).
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development