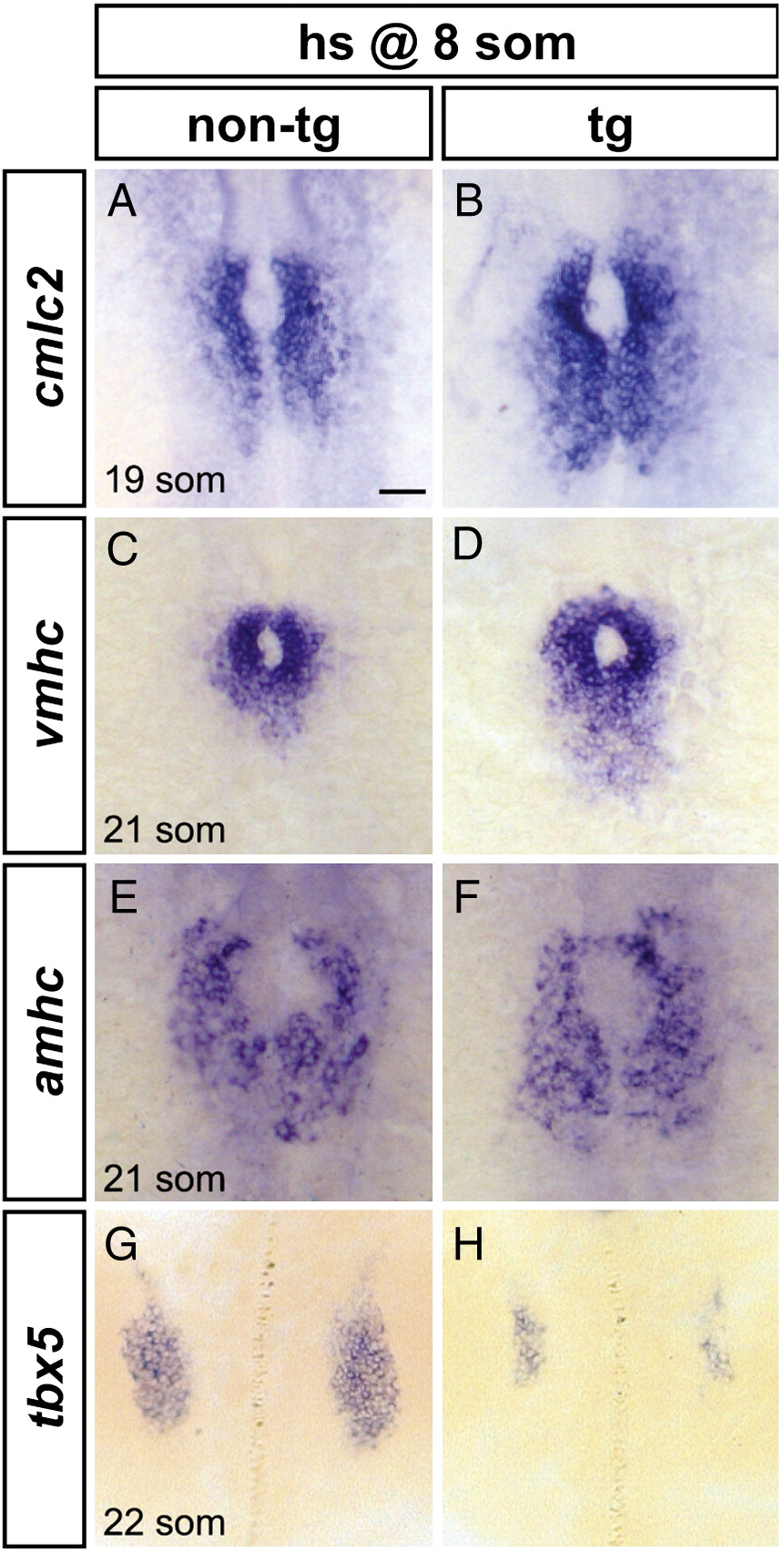
Fig. 6 Increased FGF signaling enhances formation of cardiomyocyte populations and inhibits formation of the pectoral fin field. (A?H) In situ hybridization depicts expression of cmlc2, vmhc, amhc and tbx5 at the 19-somite or 21-somite stage in non-transgenic (A, C, E, G) and Tg(hsp70:ca-fgfr1) (B, D, F, H) sibling embryos after heat shock at the 8-somite stage; dorsal views, anterior to the top. Scale bar represents 50 μm; all images are shown at the same magnification. (A, B) Ectopic FGF signaling leads to a posterior expansion of cmlc2-expressing cardiomyocytes (n = 30/37). (C, D) Ectopic FGF signaling leads to a posterior expansion of vmhc-expressing ventricular cardiomyocytes (n = 16/19). (E, F) Ectopic FGF signaling leads to a mild posterior expansion of amhc-expressing atrial cardiomyocytes (n = 8/10). (G, H) Ectopic FGF signaling leads to reduction of the pectoral fin field, as demarcated by tbx5 expression (n = 18/18).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 321(2), Marques, S.R., Lee, Y., Poss, K.D., and Yelon, D., Reiterative roles for FGF signaling in the establishment of size and proportion of the zebrafish heart, 397-406, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.