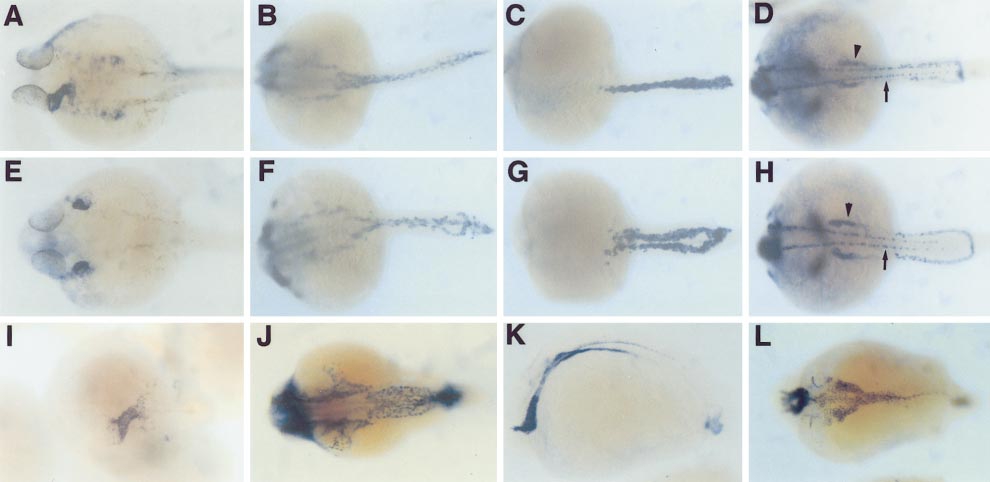
Fig. 7 Morphogenesis of several mesodermal derivatives is defective in cas mutants. Wild-type (A, B, C, D), cas (E, F, G, H), and kny (I, J, K, L) embryos showing expression of nkx2.5 (A, E, I), tie2 (B, F, J), gata1 (C, G), pax2.1 (D, H), and axial (K, L). Embryos are at 24 (A, E, I?L) and 21.5 hpf (B?D, F?H). By 24 hpf the definitive heart tube has formed in wild-type embryos (A) while two ?hearts? are evident in cas mutants (E). Pharyngeal endodermal expression of nkx2.5 is also missing in cas mutants (compare A to E). Endothelial precursors assemble smoothly in the midline of wild-type (B) but not cas mutant (F) embryos. In wild-type embryos the bilateral red blood cell precursors meet at the midline (C), but are positioned more laterally in cas mutants (G). The bilateral pronephroi (arrowheads) and pronephric ducts are also positioned more laterally in cas mutants (compare D to H); the arrows indicate the pax2.1-expressing spinal commissural interneurons. kny mutants form endoderm normally, although it is more broadly distributed (K, L); they do not exhibit cardia bifida (I); and their trunk endothelium appears smoothly although again more broadly arranged in the midline (J). All are dorsal views, anterior to the left, except (K), which is a lateral view, anterior to the left.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 215(2), Alexander, J., Rothenberg, M., Henry, G.L., and Stainier, D.Y.R., casanova plays an early and essential role in endoderm formation in zebrafish, 343-357, Copyright (1999) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.