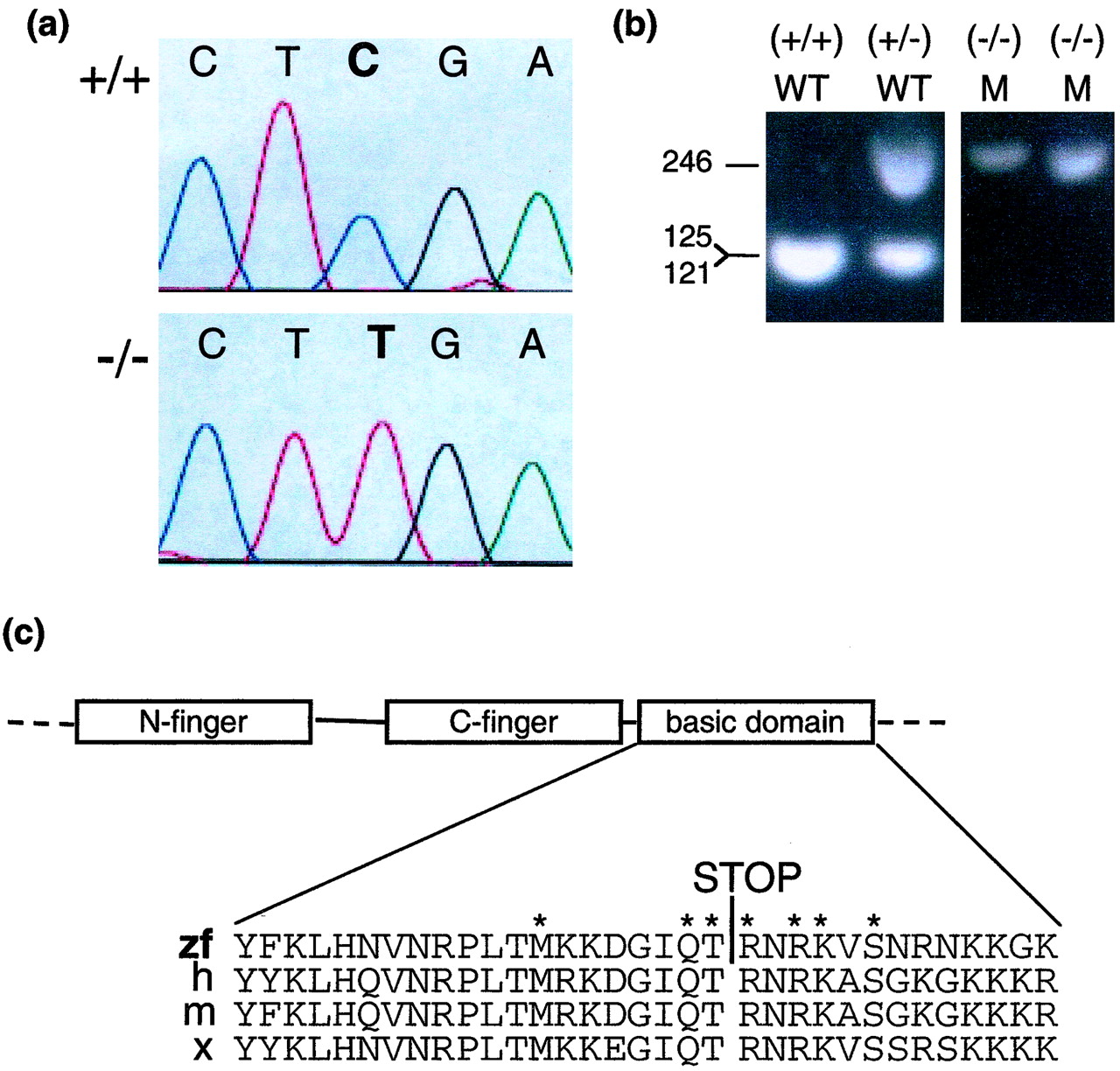
Fig. 3 Detection of a nonsense point mutation in gata1. (a) The chromatograms show sequence of PCR products derived from a homozygous wild-type embryo (+/+) (Upper) and a homozygous mutant embryo (-/-) (Lower) for the gata1 gene nt 1013-1017. (b) Genotyping of vltm651 embryos. PCR products using primers Arg-339-S and Arg-339-AS synthesized from embryo DNA of vltm651 incrosses were digested with TaqI and electrophoresed on a 2% agarose gel. After TaqI digestion, mutant alleles appear as 246-bp and wild-type alleles as 121- and 125-bp products, which migrate together in the gel shown. Phenotypically wild-type embryos (WT) identified by presence of circulating blood and phenotypically mutant (M) embryos identified by absence of circulating blood are shown. (c) A schematic representation of the N-finger, C-finger, and basic domain of Gata1 and a sequence alignment of the basic domain from different species zebrafish (zf), human (h), mouse (m), and Xenopus (x) are shown with the Arg-339 → Stop mutation identified by a STOP. The asterisks mark the aminoacids that make direct contact with the minor groove of DNA (29).
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA