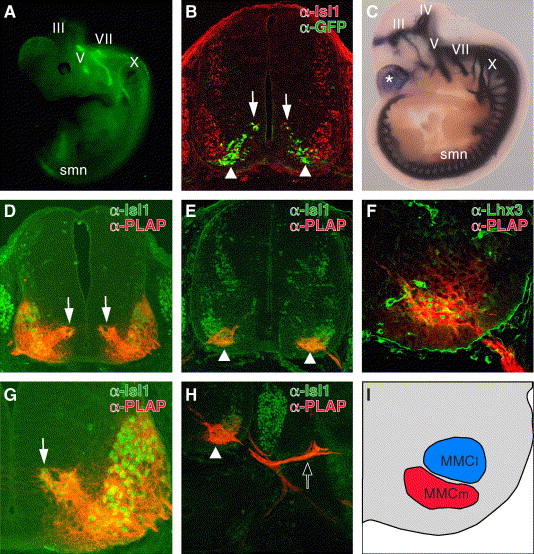
Fig. 6 Functional conservation of CREST1 for motor neuron-specific gene expression in mouse. (A) Lateral view of E11.5 Isl1-GFP transgenic mice as seen through a dissecting fluorescence microscope. III, oculomotor nerve; V, trigeminal nerve; VII, facial nerve; X, vagus nerve. This transgenic embryo carries exactly the same transgene as Isl1-GFP transgenic zebrafish (Higashijima et al., 2000). (B) Cross-section of the E11.5 Isl1-GFP embryo at the thoracic level. GFP was expressed in migrating postmitotic motor neurons (arrows) and the ventromedial subset of motor neurons (arrowheads). (C) Lateral view of the E10.5 Tg(hCREST1/isl1-PLAP) embryo stained for alkaline phosphatase activity. Both somatic and visceral motor neurons expressed PLAP at this stage. The asterisk indicates PLAP expression in the telencephalon that was commonly observed in lines examined (data not shown). IV, trochlear nerve. (D?H) Cross-sections at the thoracic level of E11.5 (D and G) and E12.5 (E, F, and H) Tg(hCREST1/isl1-PLAP) embryos double labeled with anti-Isl1 (D, E, G, and H) anti-Lhx3 (F) antibody (green) and anti-PLAP antibody (red). At E11.5 (D and G), all Isl1-positive spinal motor neurons expressed PLAP. The dorsomedially located postmitotic-migrating motor neurons (arrows) also expressed PLAP at this stage. The weak expression of PLAP in MMCl cells (F and H) may reflect this early widespread activity of CREST1. By E12.5 (E and H), PLAP expression became restricted to the ventromedial subset of Isl1-positive motor neurons (arrowheads). Note that at this stage, PLAP-positive axons projected into dorsal trunk muscles (open arrow in H). (F) All Lhx3-positive spinal motor neurons also expressed PLAP at this stage, demonstrating that the PLAP-positive neurons were the MMCm motor neurons. (I) The schematic illustration of F. The regions containing PLAP-positive MMCm neurons and PLAP-negative MMCl neurons are indicated in red and blue, respectively.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 278(2), Uemura, O., Okada, Y., Ando, H., Guedj, M., Higashijima, S., Shimazaki, T., Chino, N., Okano, H., and Okamoto, H., Comparative functional genomics revealed conservation and diversification of three enhancers of the isl1 gene for motor and sensory neuron-specific expression, 587-606, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.