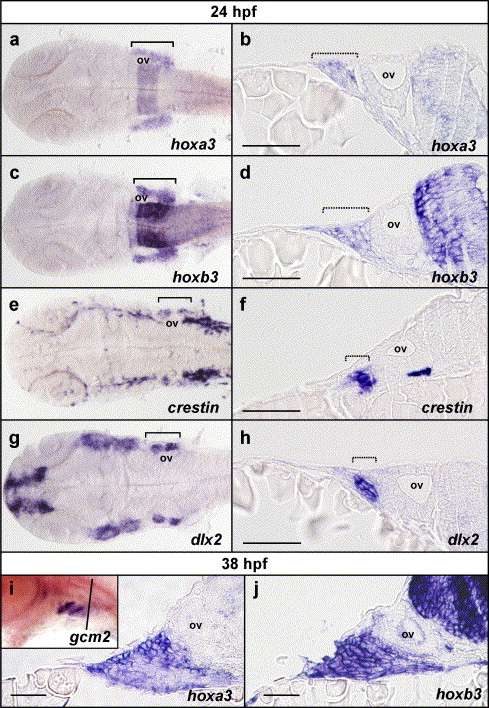
Fig. 6 Pharyngeal hoxa3 and hoxb3 expression is not restricted to the neural crest and includes external cells of the ectoderm. (a?h) Flat-mounted embryos and transverse sections of embryos post in situ hybridisation at 24 hpf for hoxa3, hoxb3, crestin and dlx2. Expression of hoxa3 (a) and hoxb3 (c) in the pharyngeal region is detected broadly throughout all of the branchial region in flat-mounted embryos. Comparison with crestin expression (e) in neural crest and dlx2 expression (g) in neural crest-derived mesenchyme reveals that hoxa3 and hoxb3 are not restricted to neural crest cells or derivatives. Transverse sections through embryos post in situ hybridisation for hoxa3 (b) and hoxb3 (d) at the level of the otic vesicle, also demonstrated that hoxa3 and hoxb3 were expressed not only in the neural crest and derivatives as marked with crestin (f) and dlx2 (h) expression, but also in the surrounding cells, which included external, ectodermal cells. (i, j). Sectional analysis of hoxa3 and hoxb3 expression post in situ hybridisation at 38 hpf revealed that expression of hoxa3 (i) and hoxb3 (j) was present in the external ectoderm during the initiation of gcm2 expression. Inset in (i) is a whole mount in situ hybridisation mount for gcm2 expression at 38 hpf, showing expression in pharyngeal arches 3 and 4 but not yet in 5 and 6, indicating that this timepoint is during the initiation of gcm2 expression (the black line indicates the approximate location of sections in i and j). ov indicates the position of the otic vesicle; brackets indicate the rostro-caudal extent of branchial staining in flat-mount preparations; and hashed brackets indicate the lateral extent of branchial staining in transverse sections. Sections are oriented with lateral to the left and medial to the right. Scale bars in b, d, f and h indicate 20 μm and in i and j indicate 10 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 276(2), Hogan, B.M., Hunter, M.P., Oates, A.C., Crowhurst, M.O., Hall, N.E., Heath, J.K., Prince, V.E., and Lieschke, G.J., Zebrafish gcm2 is required for gill filament budding from pharyngeal ectoderm, 508-522, Copyright (2004) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.