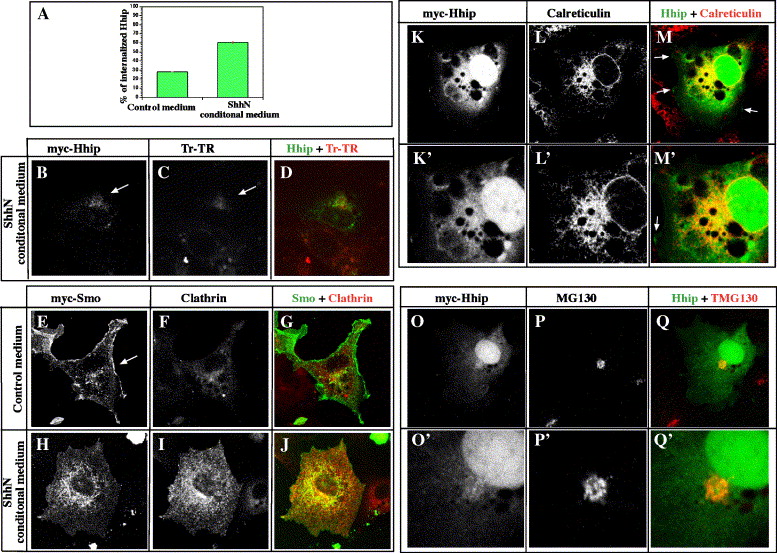
Fig. S4 Hhip protein localizes in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies. (A) Quantification of Hhip internalization in COS7 cells. COS7 cells transfected with Hhip. After incubation for 46 h, cells were treated with ShhN conditioned medium for 2 h. Cells were labeled for Hhip and endogenous Clathrin and then counted in 10 random areas (780 μm2) in each dish. The mean values from four independent dishes (± SEM) are shown. (B–D) Hhip internalizes in endosomes in response to Hh activity. Hhip transfected cells incubated with Transferrin–Alexa Fluor 594 conjugate (Tf–Alexa, Molecular Probes), a marker of early and recycling endosomes, for 30 min. (B) myc-tagged Hhip. (C) Tf–Alexa. (D) Merged image. (E–J) Smo internalizes with Clathrin in response to Hh. Smo transfected cells treated with control medium (E–G) or ShhN conditioned medium (H–J). Smo is located at the cell surface in control medium (E, arrow). In response to Hh, Smo internalizes and colocalizes with Clathrin, a marker of endocytic vesicles (H–J). Distribution of myc-tagged Smo (E, H) and Clathrin (F, I). (G, J) Merged images. (K–Q′) Hhip protein localizes in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies. (K–M′) Double labeling of myc-tagged Hhip and endogenous Calreticulin, a major endoplasmic reticulum calcium binding protein (Lynch and Michalak, 2003). Hhip protein colocalizes with Calreticulin (M, M′). Arrows indicate membrane localized Hhip (M, M′). (K′–M′) Magnified views of cells shown in K–M. (O–Q′) Double labeling of Hhip and endogenous GM130, a marker for Golgi bodies (Barr and Short, 2003). GM130 functions as a structural element of the Golgi apparatus and also provides attachment sites for membranes and other Golgi proteins. (O′–Q′) Magnified views of cells shown in O–Q. (B–Q′) Single confocal images.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 297(1), Ochi, H., Pearson, B.J., Chuang, P.T., Hammerschmidt, M., and Westerfield, M., Hhip regulates zebrafish muscle development by both sequestering Hedgehog and modulating localization of Smoothened, 127-140, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.