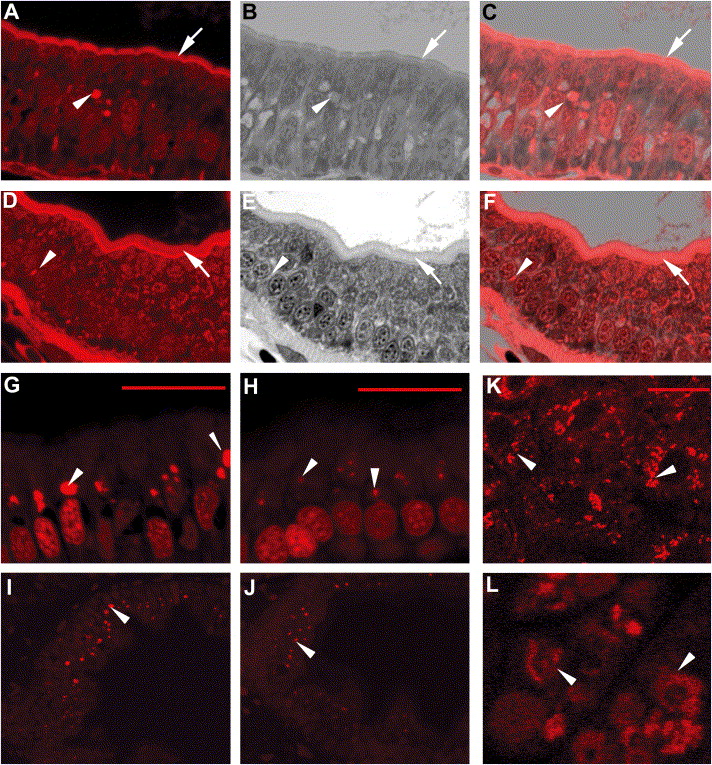
Fig. 7 ffr mutants exhibit altered vesicular trafficking and APOA1 targeting A–F) Histological cross-sections through the intestine of 5 dpf ffr (A–C) and wild-type (D–F) larvae. Red fluorescence shows AM1-43 accumulation in plasma membrane (arrows) and intracellular vesicles (arrow head) in ffr mutant and wild-type enterocytes. (B and E) Identical sections in (A) and (D) stained with 1% methylene blue in 1% sodium borate and 1% Azure B (1:1). (C and F) Composites of panels (A) and (B), and (D) and (E), respectively. Note accumulation of AM1-43 in the region of the Golgi of ffr enteroctyes (C). This is best appreciated in histological cross-sections through the intestine of 5 dpf ffr and wild-type larvae following AM1-43 ingestion and cyclodextran wash to remove noninternalized dye within the plasma membrane (G–J). (K–L) Following ffr “knockdown” by MO-1, the apoA1-mRFP fusion protein had a diffuse intracellular distribution (arrowhead in [L]), whereas in control embryos the apoA1-mRFP fusion protein was present within vesicles surrounding the nucleus (arrowhead). The scale bar represents 15 μm.
Reprinted from Cell Metabolism, 3(4), Ho, S.Y., Lorent, K., Pack, M., and Farber, S.A., Zebrafish fat-free is required for intestinal lipid absorption and Golgi apparatus structure, 289-300, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Cell Metab.