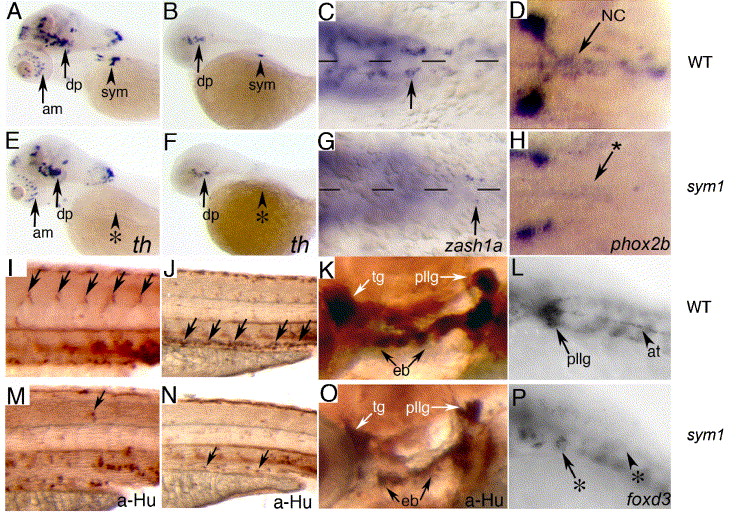
Fig. 1 sym1 mutants have defects in trunk and vagal neural crest-derived peripheral neurons, cranial ganglion neurons and glia. Lateral views of wild-type (A, B) and sym1 mutant (E, F) embryos showing tyrosine hydroxylase (th) expression at 5 dpf (A, E) and 48 hpf (B, F). There is a dramatic reduction in the number of th-positive cells in the region of the developing sympathetic cervical complex (arrowheads) in sym1 mutants (0–2 cells at 2 dpf, 0–10 cells at 5 dpf, n = 10), compared to their wild-type siblings (10–15 cells at 2 dpf, 40–50 cells at 5 dpf, n = 10). High magnification ventral views of wild-type (C, D) and sym1 mutant (G, H) embryos, showing that the loss of sympathetic neurons in sym1 mutants is reflected by a severely reduced number of sympathoblasts based on zash1a expression at 40 hpf (C, G) and phox2b expression at 48 hpf (D, H). Arrows in C, D, G, H indicate migrating sympathoblasts. Lateral views of wild-type (I–L) and sym1 mutant (M–P) embryos. Black arrows indicate position of developing DRG (I) and enteric neurons (J) in 3 dpf wild-type embryos, which are largely absent in sym1 mutants (M, N). The cranial ganglion neurons at 3 dpf are reduced in size in sym1 mutants by approximately 30% (K compared to O). White arrows indicate the trigeminal (tg) and posterior lateral line (pllg) ganglia complex. Black arrows indicate epibranchial ganglia (eb). (L, P) foxd3 is expressed in developing glia associated with the posterior lateral line ganglia (arrow) and axon tract (arrowhead) in wild-type embryos at 48 hpf (L), but is severely reduced or absent in sym1 mutant embryos (P). Abbreviations: absence of expressing cells (*), amacrine cells (am), axon tract (at), dopaminergic neurons (dp), hindbrain (hb), neural crest-derived enteric and sympathetic precursors (NC), sympathetic neurons (sym).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 292(1), Stewart, R.A., Arduini, B.L., Berghmans, S., George, R.E., Kanki, J.P., Henion, P.D., and Look, A.T., Zebrafish foxd3 is selectively required for neural crest specification, migration and survival, 174-188, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.