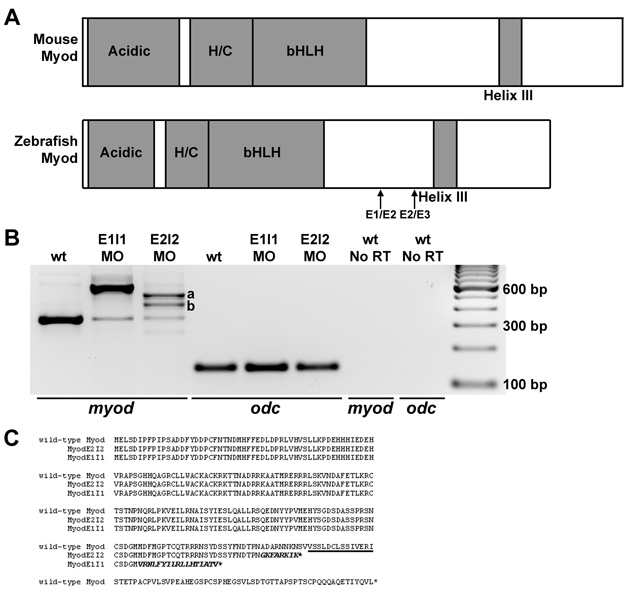
Fig. S3 myod splice-blocking and translation-blocking morpholinos knock down normal myod mRNA or protein levels. (A) Diagrams of functional domains of Myod, including the acidic activation domain, and the histidine- and cysteine-rich domain (H/C). The amino acid sequence of helix III is 100% identical between zebrafish, mouse and human. Exon 1-exon 2 (E1/E2) and exon 2-exon 3 (E2/E3) junctions are shown. (B) RT-PCR analysis of myod mRNA products (using primers in exon 1 and exon 3) from wild-type control, myod-splMO E1I1 and myod-splMO E2I2 embryos. E1I1 targets the myod exon 1-intron 1 boundary and E2I2 targets the exon 2-intron 2 boundary. cDNA sequencing confirms that the E1I1 splice variant retains intron 1 and the E2I2 splice variants retain all (variant a) or most (variant b) of intron 2. qRT-PCR shows that less than about 10-15% of normally spliced myod transcripts remain in myod-splMO embryos (Figs 2P and S3 and data not shown), whereas the total level of myod mRNA remains similar or increased compared to that in control embryos (Fig. S3 and data not shown). (C) Predicted amino acid sequences based on cDNA sequencing of splice variants. Helix III domain is underlined; amino acid sequence from translated intron sequences are shown in italics. When intron 1 or intron 2 splicing is inhibited, in-frame stop codons in intron 1 or intron 2 predict the generation of truncated Myod proteins lacking helix III. E2I2 variants a and b share the same intron sequence up to the stop codon. (D-G) Mammalian anti-Myf5 antibody (which detects zebrafish Myod protein; Hammond et al., 2007) staining in (D) control, (E) myod-MO, (F) myod-splMO E1I1, and (G) myod-splMO E2I2 embryos. The anti-Myf5 antibody was generated against the C-terminus of the protein. Therefore, although myod-splMO embryos appear to have little or no wild-type Myod protein, we cannot determine whether the predicted truncated product is present.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development