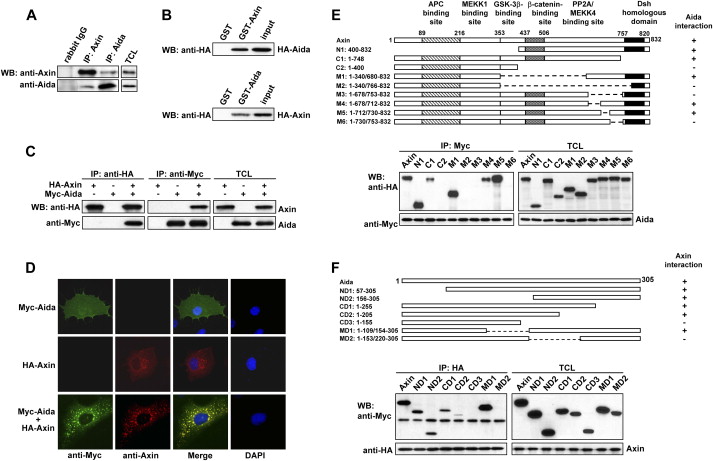
Fig. 1 Identification of Aida as an Axin Interaction Partner (A) Endogenous Axin and Aida interact with each other. Axin and Aida in untransfected C2C12 cells were immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti-Axin and anti-Aida, respectively. Rabbit IgG was used as control. Detection of Axin and Aida in the immunoprecipitates and total cell lysates (TCLs) was carried out using anti-Axin and anti-Aida antibodies, respectively. (B) GST pull-down assay to evaluate Axin interaction with Aida in vitro. The ability of GST-Axin to retain Aida present in the cell lysate from HEK293T cells transfected with pCMV-HA-Aida was analyzed by western blotting with anti-HA (upper panel). GST-Aida specifically pulled down HA-Axin in the cell lysate (lower panel). In either case, GST alone did not interact with Aida or Axin. Input represented one-sixth of lysate used for GST pull-down. (C) Axin and Aida interact with each other when overexpressed in HEK293T cells. HA-Axin and Myc-Aida were expressed in HEK293T cells singly or in combination. Reciprocal coimmunoprecipitation was performed by using anti-HA or anti-myc antibody followed by immunoblotting using anti-Myc or anti-HA antibody as indicated. (D) Colocalization of Axin and Aida in mammalian cells. COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with myc-Aida and Axin and stained for Axin (red) and Aida (green) using rhodamine conjugated mouse antibody and FITC conjugated rabbit antibody, respectively. (E) Aida interacts with a specific C-terminal domain of Axin. Schematic diagrams depict different Axin deletion mutants used in the domain-mapping experiments. Different HA-tagged Axin deletion constructs were transiently transfected into HEK293T cells together with Myc-tagged Aida. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody, followed by immunoblotting using anti-HA for Axin proteins and anti-Myc for Aida. (F) Determination of Axin binding sites in Aida. Shown on the top are schematic diagrams of different Aida deletion mutants used in the domain-mapping experiments. Same experiments were performed as described in (E).
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 13(2), Rui, Y., Xu, Z., Xiong, B., Cao, Y., Lin, S., Zhang, M., Chan, S.C., Luo, W., Han, Y., Lu, Z., Ye, Z., Zhou, H.M., Han, J., Meng, A., and Lin, S.C., A beta-Catenin-Independent Dorsalization Pathway Activated by Axin/JNK Signaling and Antagonized by Aida, 268-282, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell