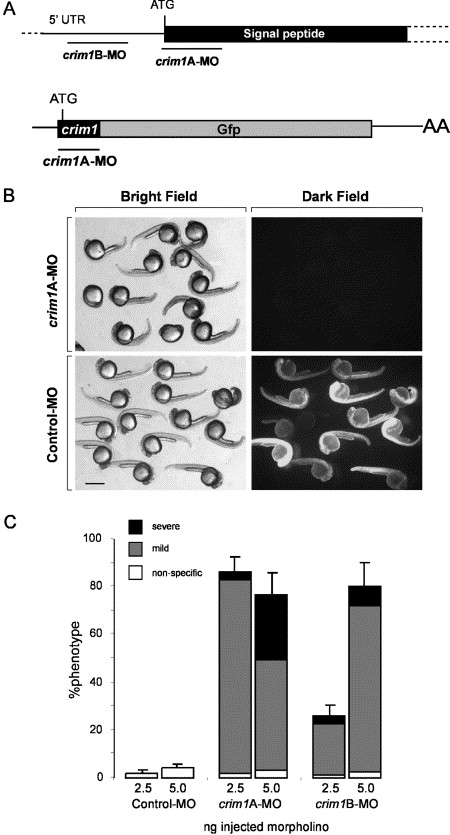
Fig. 2 Morpholino knockdown of zebrafish crim1. (A) Schematic showing the position of morpholino oligos designed across the start codon and (crim1A-MO) and to a region of the 5′ UTR (crim1B-MO) of zebrafish crim1 mRNA. To test the ability of crim1A-MO to knockdown expression of its target sequence, a Gfp reporter construct was produced. The start codon and first seven amino acids encode zebrafish crim1 sequence. (B) Brightfield and darkfield images showing that crim1A-MO but not a randomised control morpholino can block the production of GFP protein in zebrafish embryos injected with 500 pg of crim1-Gfp chaemeric mRNA. Scale bar=500 μm. (C) Graph showing the distribution of phenotypes observed by injection of 2.5 or 5 ng of control, crim1A-MO or crim1B-MO. Mild are embryos as represented in gray and severe in black. Standard error is deviation between separate injection experiments (n=4, 50?100 embryos/experiment).
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 123(4), Kinna, G., Kolle, G., Carter, A., Key, B., Lieschke, G.J., Perkins, A., and Little, M.H., Knockdown of zebrafish crim1 results in a bent tail phenotype with defects in somite and vascular development, 277-287, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.