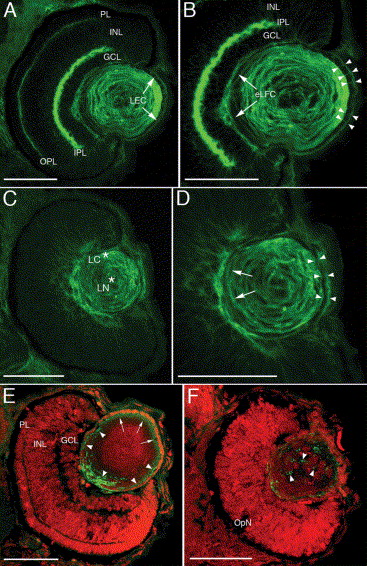
Fig. 6 Actin fails to localize properly in the morphant lens epithelial cells. Phalloidin-AlexaFluor 488 (A–D) was used to stain the filamentous actin in lenses and retinas of wild type (A, B) and morphants (C, D) at 3 dpf. In the control lens, actin is localized in a concentric pattern associated with the fiber cell membranes in both the nuclear and cortical regions (A, B). Lens epithelial cells (A, LEC) exhibit actin localization to both the distal (basal) and lateral aspects of the individual epithelial cells (B, arrowheads). Actin staining of the morphant lens reveals poorly defined elongating fiber cells (D, arrows) and a diffuse actin network in the lens epithelial cells (D, arrowheads). The sections also reveal intense actin staining within the retinal inner (IPL) and outer (OPL) plexiform layers (A, B), which is absent in the morphant (C). The lens-specific zl-1 monoclonal antibody labels the cortical region of the wild-type lens (E, arrowheads) and is localized near the apical–apical interface between the epithelial and fiber cells (E, arrows). In the morphant (F), the zl-1 protein is scattered throughout the lens and appears to be associated with the nucleated fiber cells (arrowheads). Abbreviations: PL, photoreceptor layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; LEC, lens epithelial cells; eLFC, elongating lens fiber cells; OpN, optic nerve. Scale bars represent 50 μm.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 122(4), Shi, X., Bosenko, D.V., Zinkevich, N.S., Foley, S., Hyde, D.R., Semina, E.V., and Vihtelic, T.S., Zebrafish pitx3 is necessary for normal lens and retinal development, 513-527, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.