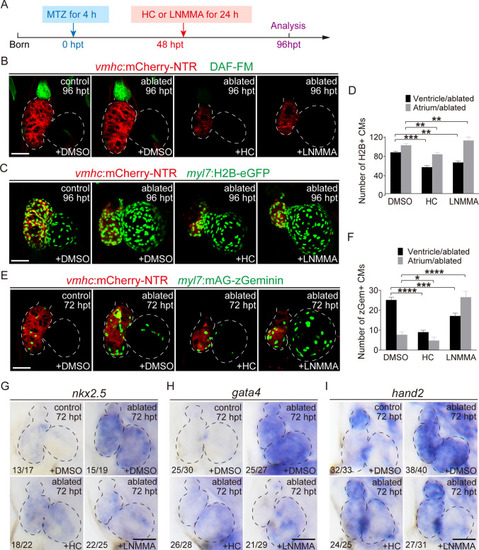
Trpv4 and NO signaling play essential roles in the late stage of ventricle regeneration. A Schematic timeline diagram of MTZ treatment to induce ventricle ablation and HC-067047 treatment to inhibit Trpv4 or L-NMMA treatment to inhibit NO synthesis. B DAF-FM DA staining of Tg(vmhc:mCherry-NTR) larvae at 96 hpt revealed that HC-067047 or L-NMMA treatment for 48–72 hpt blocked NO production. C Confocal images of control and ablated hearts treated with DMSO, HC-067047 or L-NMMA for 48–72 hpt in Tg(vmhc:mCherry-NTR; myl7:H2B-eGFP) larvae at 96 hpt. D Quantification of H2B+ CM numbers in DMSO-, HC-067047- and L-NMMA-treated ablated hearts. N = 19, 15, 10, respectively. Mean + s.e.m. ANOVA analysis; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. E Confocal images of control and ablated hearts treated with DMSO, HC-067047 or L-NMMA for 48–72 hpt in Tg(vmhc:mCherry-NTR; myl7:mAG-zGeminin) larvae at 72 hpt. F Quantification of zGeminin+ CM numbers in DMSO-, HC-067047- and L-NMMA-treated ablated hearts. N = 17, 10, 15, respectively. Mean + s.e.m. ANOVA analysis; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. G–I Whole-mount in situ hybridizations showed reduced expression of nkx2.5, gata4 and hand2 at 72 hpt in control and ablated hearts treated with DMSO, HC-067047 or L-NMMA for 48–72 hpt. Numbers indicate the ratio of representative staining observed. Scale bars, 50 μm. Dashed lines outline the hearts. hpt hours post treatment, NO nitric oxide, CM cardiomyocyte, V ventricle, A atrium, HC HC-067047
|

