Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-231122-22
- Publication
- Lencer et al., 2023 - Mutations in cdon and boc affect trunk neural crest cell migration and slow-twitch muscle development in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
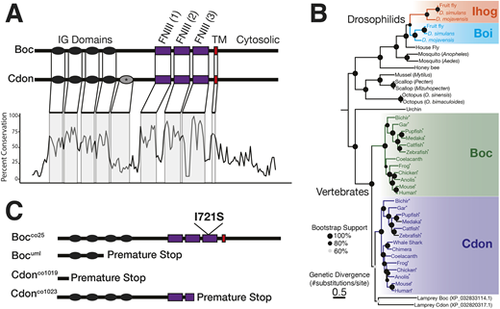
cdon and boc are transmembrane receptors and share conserved domain structure. (A) cdon and boc share a domain structure of four or five immunoglobin (IG) domains, three fibronectin (FNIII) domains, a transmembrane (TM) region and a cytosolic C-terminal tail. A fifth cdon IG domain (*) is found in some tetrapod taxa. Percent conservation (20 amino acid sliding window) is shown for an alignment of cdon and boc amino acid sequences from 11 tetrapod and ray-finned fish taxa. The extracellular domains exhibit high sequence conservation, while the cytosolic region is less conserved. (B) Maximum likelihood tree (phyml) for curated cdon and boc ortholog amino acid sequences from multiple bilaterian taxa. There are independent duplications of Ihog/Boi in drosophilids and of Cdon/Boc in vertebrates. Node support was calculated based on 1000 bootstraps; nodes with less than 60% bootstrap support are shown in gray. Asterisks indicate taxa used to generate conservation in A. Lamprey cdon and boc sequences are uncolored due to topological position as an outgroup with respect to vertebrate cdon sequences. (C) Schematic of cdon and boc mutant alleles characterized in the current study. |