FIGURE 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230228-297
- Publication
- Ghosal et al., 2023 - Embryonic ethanol exposure disrupts craniofacial neuromuscular integration in zebrafish larvae
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
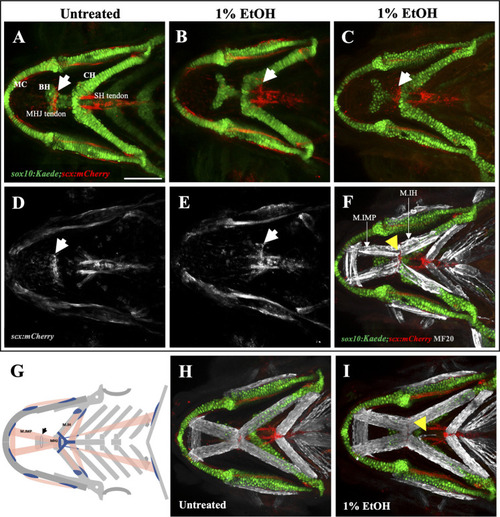
Ethanol can mislocate myotendinous attachment tissues (A, D) Ventral view of branchial cartilage and tendon in untreated sox10:Kaede;scx:mCherry fish at 4dpf. Arrows show the normal position of the MHJ (mylohyoid junction) around the anterior basihyal. (B,C, E) Posteriorized MHJ position in ethanol-exposed sox10:Kaede;scx:mCherry fish at the level of SHT (sternohyoideus tendon) in (B, E) and at the anterior end of ceratohyal in (C) (F) Ethanol-exposed sox10:Kaede;scx:mCherry fish immunostained with MF20 (gray), anti-Kaede (green) and anti-mCherry (red) antibodies. Arrow shows that the posterior end of the Intermandibularis posterior muscle (M.IMP) aligns with the MHJ tendon and is located at the level of ceratohyal. (G) Schematic showing posteriorized MHJ tendon and Intermandibularis posterior muscle (M.IMP). Arrow indicates the normal position of the MHJ tendon. |