|
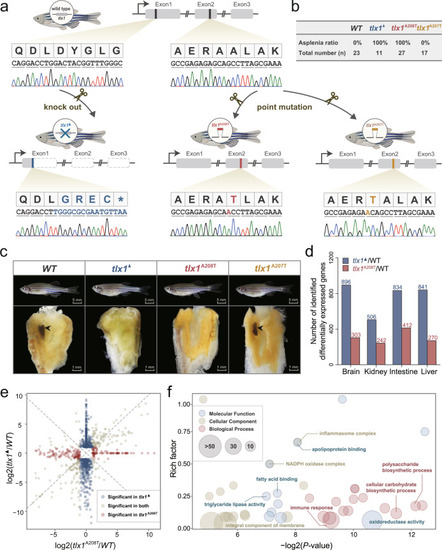
Missense mutation of tlx1 controls asplenia phenotype in zebrafish. Missense mutation of <italic>tlx1</italic> controls asplenia phenotype in zebrafish.a Genome editing of three zebrafish lines (tlx1▲, tlx1A208T and tlx1A207T) using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Procedures are detailed in Supplementary Fig. 15. ▲ represents full knockout of the gene, while A208T and A207T indicate the specific point mutations at sites 622 and 619 of zebrafish tlx1, respectively. Blue, tlx1▲; Red, tlx1A208T; Yellow, tlx1A207T. The tlx1 nucleotide sequence of genomic DNA of three zebrafish lines was validated by Sanger sequencing. The figure was created with BioRender.com. b, ctlx1▲ and tlx1A208T zebrafish exhibited asplenia while tlx1A207T zebrafish had an intact spleen; the asplenia ratio of individuals was calculated and listed (n = 11~23). The splenic phenotype of other 74 individuals were listed in Supplementary Figs. 16–18. WT wild type. d Differentially expressed gene (DEG) number of tlx1▲ and tlx1A208T compared to that of wild-type individuals via comparisons of the brain-, kidney-, intestine-, and liver-transcriptomes. e Volcano map of the shared and group-specific DEGs in the brain of tlx1▲ and tlx1A208T compared to that in the wild-type group. Blue, red, and gray represent significantly changed DEGs in tlx1▲, tlx1A208T, and both groups, respectively. f GO enrichment of the DEGs between tlx1▲ and tlx1A208T illustrate the different in gene expression patterns associated with brain development and function. The enrichment was conducted using the GOseq R package, and corrected P < 0.05 indicated significant enrichment. The size of the circle represents the number of genes in each category. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
|