Figure 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221214-30
- Publication
- Faustini et al., 2022 - Synapsin III Regulates Dopaminergic Neuron Development in Vertebrates
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
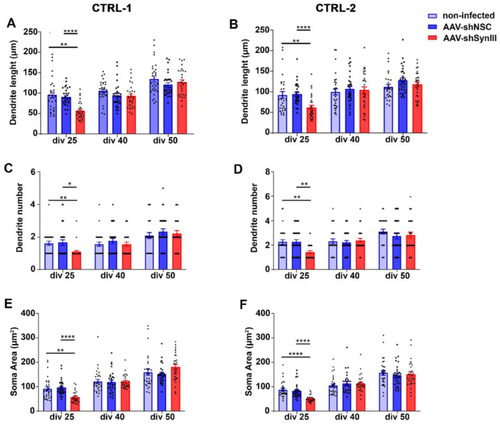
AAV-mediated Syn III RNAi impaired early iPSCs-derived mDN development. (A,B) Graphs show primary dendrite length analysis (expressed in Ám) in control non-infected AAV-shSynIII- or AAV-shNSC-infected mDN produced from CTRL-1 (A) and CTRL-2 (B) iPSCs clones at div 25, 40 and 50. At 25 div AAV-shSynIII-infected mDN showed a statistically significant decrease in primary dendrite length when compared to NI and AAV-shNSC-infected cells (** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.001; two-way ANOVA + Bonferroni?s post-test). No changes were observed at div 40 or 50. n = 30 cells per each experimental condition. (C,D) Graphs show dendrites number in control and AAV-shSynIII- or AAV-shNSC-infected mDN produced from CTRL-1 (C) and CTRL-2 (D) iPSCs clones at div 25, 40 and 50. A significant decrease in the number of dendrites at div 25 was observed in the AAV-shSynIII-infected mDN when compared to both control and AAV-shNSC-infected cells (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; two-way ANOVA + Bonferroni?s post-test). No changes were observed at div 40 or 50. n = 30 cells per each condition. (E,F) Graphs show the analysis of soma area of mDN (expressed in Ám2) from control and AAV-shSynIII- or AAV-shNSC-infected mDN produced from CTRL-1 (E) and CTRL-2 (F) iPSCs clones at div 25, 40 and 50. A significant decrease in the mean soma area was detected in the AAV-shSynIII-infected mDN at div 25 when compared to control (** p < 0.01 and **** p < 0.0001) or AAV-shNSC-infected cells (**** p < 0.0001). Two-way ANOVA + Bonferroni?s post-test). No changes were observed at div 40 or 50. n = 30 cells per each condition. |