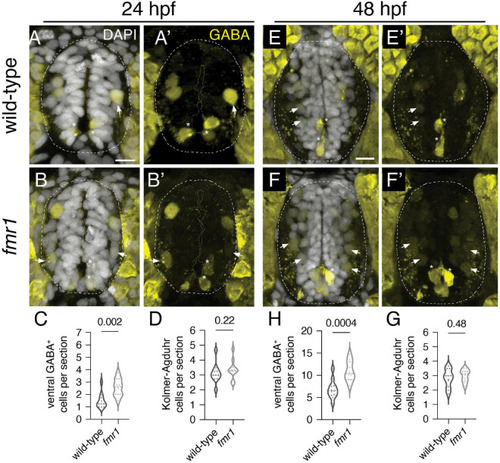
Fmrp restricts the production of GABAergic cells in the ventral spinal cord. Immunohistochemistry to detect gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at 24 h post-fertilization [hpf; (A,B) and (A?,B?)] and 48 hpf (E,F) and (E?,F?) on transverse sections of trunk spinal cord reveals two populations of ventral GABA+ interneurons (INs): robustly GABA-expressing Kolmer?Agduhr (KA) INs (asterisks) that line the central canal (outlined in yellow dashed line) and a group of more weakly-expressing GABA+ INs positioned in the ventrolateral spinal cord (arrowheads). This GABA antibody produces a bright artifact outside of the spinal cord, and the cord is therefore outlined in a dashed oval in DAPI-merged images. Quantification of ventral GABA+ cells at 24 hpf [(C); two-tailed t-test] and 48 hpf [(G); two-tailed t-test], and KA neurons at 24 hpf [(D); Mann?Whitney test] and 48 hpf [(H); two-tailed t-test]. Quantification reflects the average number of cells per section, averaged by embryo. Scale bar = 10 ?m. P-values indicated in graphs, where p < 0.05 is considered significant.
|

