Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220829-241
- Publication
- Pan et al., 2022 - Essential Roles of the Histone Demethylase KDM4C in Renal Development and Acute Kidney Injury
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
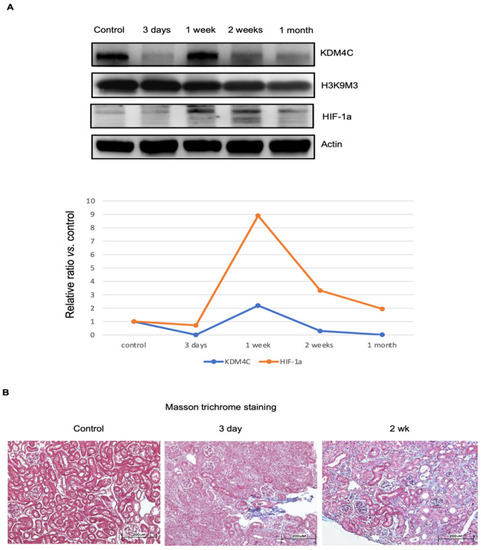
Temporal changes in KDM4C and progression of kidney fibrosis during kidney injury. Wild-type mice receiving kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) were used for this study. Kidney tissues, after IRI for the durations indicated in the figure, were harvested (n = 8 for each group). (A). Western blotting results for KDM4C, H3K9M3, and HIF-1α. The average relative ratios of KDM4C and HIF-1α along the course of injury are shown. (B). Masson trichrome staining results of kidney tissues after IRI. Mild glomerulous and tubulointerstitial fibrosis, 3 days after receiving IRI-AKI. The severity of glomerulous and tubulointerstitial fibrosis was even more pronounced 2 weeks after IRI-AKI. Abbreviation: HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; KDM4C, Lysine demethylase 4C. |