Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220627-54
- Publication
- Xue et al., 2022 - HOX epimutations driven by maternal SMCHD1/LRIF1 haploinsufficiency trigger homeotic transformations in genetically wildtype offspring
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
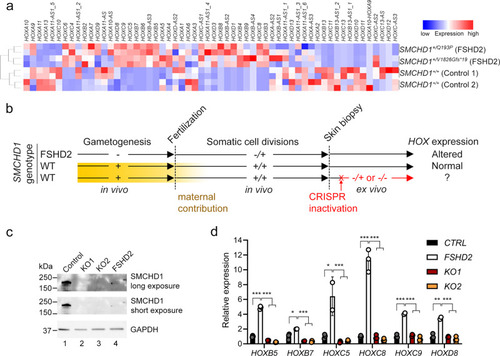
Germline, but not adult, SMCHD1 deficiency leads to HOX dysregulation in human cutaneous fibroblasts.
a RNA-seq performed on controls and FSHD2 patient fibroblasts reveal dysregulations of HOX expression when SMCHD1 was mutated in the germline. b Schematic of experimental design to determine whether HOX dysregulation is the result of germline or somatic SMCHD1 haploinsufficiency. SMCHD1 was CRISPR/ Cas9-inactivated ex vivo in control fibroblasts using two distinct guide RNAs (KO1 and KO2). Yellow box represents maternal contribution of SMCHD1 which diminishes rapidly post-fertilization. c Western blot in fibroblasts cell extract show successful knockout of SMCHD1, resulting in protein-null alleles. FSHD2 cells used here are?+?/V1826Gfs*19. d qPCR shows that, unlike in FSHD2 cells, somatic knockout of SMCHD1 in adult cells does not lead to the upregulation of HOX. P values were calculated by 2-tailed unpaired Student?s t test. *p?<?0.05, **p?<?0.01, ***p?<?0.001. Data are presented as mean values?±?SD. |