Figure 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-211216-11
- Publication
- Kim et al., 2021 - The effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors on organ-specific ace2 expression in zebrafish and its implications for COVID-19
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
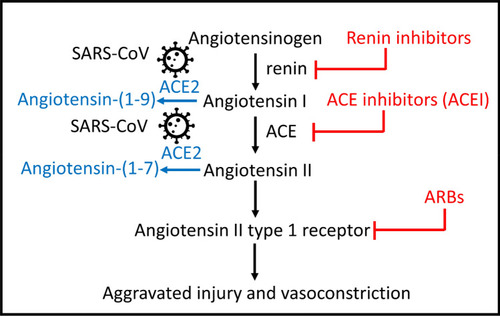
The RAAS pathway and its relationship to SARS-CoV(1 and 2) viruses. Upon entry to cells, the SARS-CoV is known to bind to its functional receptor, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). In normal physiology, renin cleaves angiotensinogen, produced by the liver which yields angiotensin I. The angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II and the angiotensin II binds to the angiotensin II type 1 receptor which leads to vasoconstriction, aggravated tissue injury and hormonal production. ACE2 cleaves angiotensin II into angiotensin (1–7) to attenuate the effects of vasoconstriction. Another function of ACE2 involves cleaving angiotensin I to angiotensin-(1–9) for the hydrolysis of peptides such as apelin-1. Aliskiren is a direct renin inhibitor that blocks the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. Captopril is an ACE-I that blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Olmesartan is an ARB ACE-I: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor, ARB: Angiotensin Receptor Blocker, ACE: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-1, ACE2: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2. |