Figure 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210813-8
- Publication
- Park et al., 2021 - Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
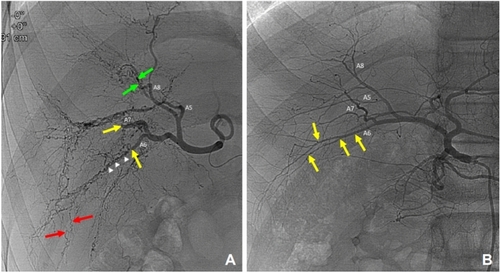
Comparison of visceral angiograms between the patient’s hepatic artery ( |