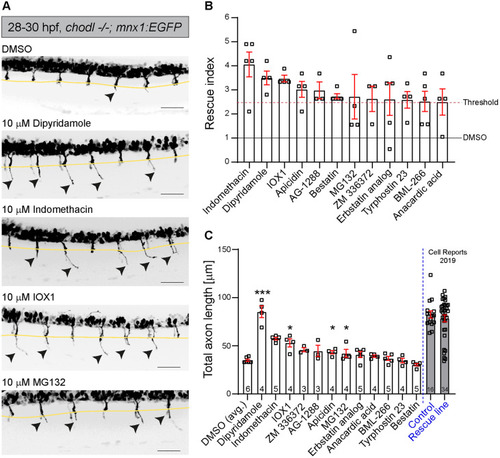
Several compounds significantly increase the number of axons that grow beyond the HM. (A) Representative VAST images of 28-29 hpf drug-treated chodl mutant embryos. Arrowheads indicate CaP motor axons beyond the HM (yellow line). Scale bars: 50 µm. (B) The 12 compound hits with the highest rescue index, presented according to the percentage of motor axons that crossed the HM in comparison to that of internal control (DMSO-chodl mutant). Compounds were tested at 10 µM. Each data point represents one animal. Error bars represent means±s.e.m. (C) The 12 compound hits are ranked according to the total length of CaP motor axons after compound application. The average length of CaP motor axons in DMSO-chodl mutant is 35.06 µm. Statistical tests were performed, comparing the drug treatment with its own DMSO-chodl mutant control (dipyridamole, Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison test ***P=0.0009, statistical power=0.999; IOX1, Mann–Whitney test *P=0.0159, statistical power=0.9750; MG132, Mann–Whitney test *P=0.0242, statistical power=0.9620; apicidin, Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison test *P=0.0306, statistical power=0.9564). Grey bars represent previously published data (Opris¸oreanu et al., 2019), and are used to estimate the effect of various compounds on the length of CaP motor axons compared to that in wild-type embryos (Control) and chodl mutant embryos, in which the phenotype was rescued by stable overexpression of chodl in motor neurons (Rescue line). Each data point represents one animal, n-numbers are indicated in each bar. Error bars represent means±s.e.m.
|

